22 Fun Facts About Space | Beyond the Stars
1. Space is a three-dimensional continuum containing positions and directions.
Space is an endless, three-dimensional playground where all the events and objects in the universe find their place and direction. It’s more than just up, down, or sideways; it’s everywhere, and when you add time to the mix, it becomes spacetime.
This vast stage is where every space fact comes to life, showing us where things are and how they move in this grand expanse.
2. A full NASA space suit costs $12,000,000.
A full NASA spacesuit costs an astonishing $12,000,000. Tested in North Dakota’s badlands, the suit weighs 47 pounds without its life support backpack. Surprisingly, the gloves are the most expensive part.
Designing these suits is complex; they’re essentially personal spacecraft, equipped with advanced life support and safety systems, justifying their hefty price tag.
3. After the Big Bang, space was dense, hot plasma, rapidly expanding.
Right after the Big Bang, space was a seething cauldron of hot, dense plasma, expanding swiftly. In this early chaos, temperatures were so extreme that not even atoms or their nuclei could stay intact, creating a soup of quarks and gluons.
From a tiny, infinitely dense point, space itself stretched outward faster than light, cooling down to form the vast universe we explore today, about 13.7 billion years ago.
4. Hubble Space Telescope can see back in time to 13.4 billion years ago.
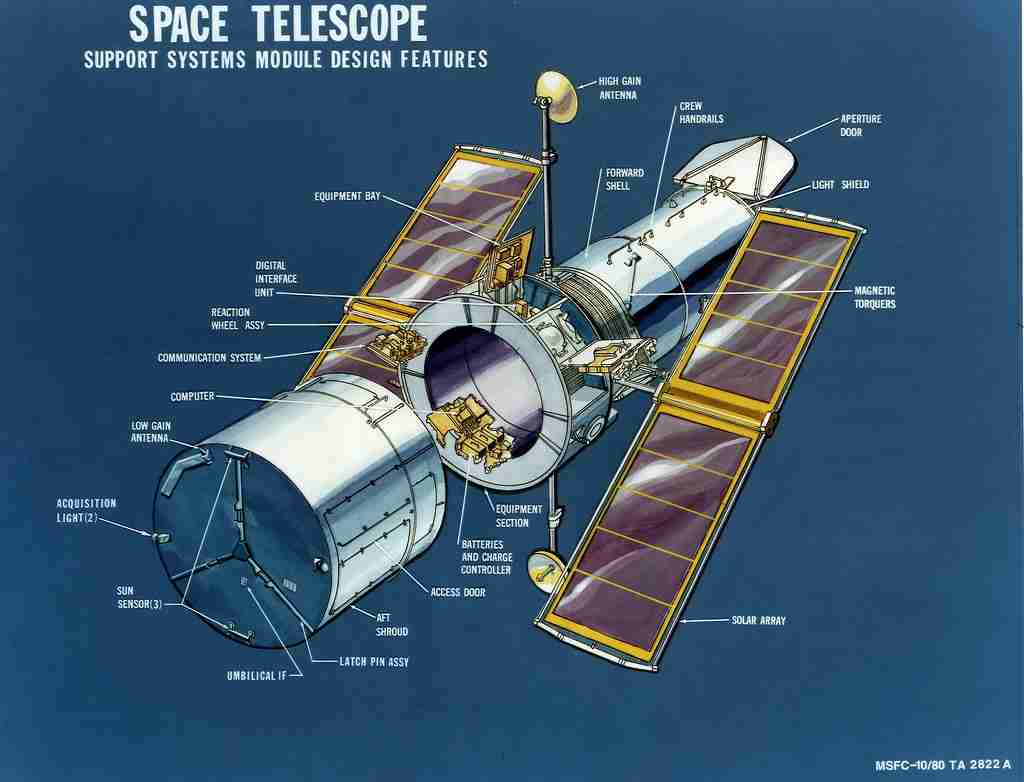
Launched in 1990, the Hubble Space Telescope has revolutionized our view of the universe, capturing stunning images of distant galaxies and nebulae. Its powerful lens allows us to look back in time to about 13.4 billion years ago, just after the Big Bang.
Hubble’s contributions to science are immense, with over 15,000 published papers and 738,000 citations, making it an invaluable tool for astronomers.
5. Nobody knows how many stars are there in space.
Estimating the universe’s vastness, astronomers suggest there might be around 200 billion trillion stars, making space a realm of endless wonder. This number comes from multiplying the Milky Way’s stars by the galaxies we know exist.
Yet, despite these deep space facts, the true star count remains a mystery, showcasing the universe’s incomprehensible scale and beauty.
6. Space-time began with the Big Bang, as per the theory of general relativity.
Albert Einstein’s general theory of relativity, formulated in 1916, revolutionized our understanding of space and the universe’s origins. It suggests that space-time, the fabric of the cosmos, began with the Big Bang.
This theory, with its elegant mathematical framework, explains how matter influences space-time’s curvature, leading to the conclusion that the universe is not static but expanding.
7. Why can’t sound travel in space?
Space is silent because it’s a vacuum with no air for sound to travel through. While you can’t hear anything in the emptiness of space, astronauts can still talk to each other using radios.
This is because radio waves, unlike sound, don’t need air to move, allowing communication across the vast, quiet expanse of space.
8. Space has a water cloud with 140 trillion times Earth’s ocean water.
One of the creepy facts about space is the existence of a colossal water vapor cloud, floating 12 billion light-years away, surrounding a quasar.
This cloud holds 140 trillion times the mass of all Earth’s oceans combined, making it the universe’s largest known water reservoir. Astonishingly, it weighs more than 40 billion times the weight of Earth.
9. The International Space Station circles Earth every 92 minutes.
The International Space Station (ISS) orbits Earth every 92 minutes at a speed of 17,150 miles per hour, allowing its crew to experience 16 sunrises and sunsets each day.
Home to an international crew of seven, the ISS completes 16 orbits of Earth in 24 hours, providing a unique perspective on the planet and the cosmos beyond.
10. The first woman in space was a Russian called Valentina Tereshkova.
Valentina Tereshkova, a Soviet cosmonaut, made history as the first woman in space on 16 June 1963, launching from Baikonur Cosmodrome, Kazakhstan. During her solo mission on Vostok 6, she orbited Earth 48 times and spent nearly three days in space.
Known by her radio nickname “Chaika,” meaning seagull, Tereshkova paved the way for women in space exploration.
11. What was the first soft drink in space?
Another lesser-known space fact is Coca-Cola holds the title of the first commercial soft drink consumed in space. This milestone occurred in 1985 when astronauts aboard the Space Shuttle Challenger used a specially designed Coca-Cola Space Can.
Following this, the Space Shuttle Discovery featured the first-ever ‘Space Dispenser,’ further cementing Coca-Cola’s place in space exploration history during a memorable moment on NASA’s STS-63 mission.
12. In 4 billion years, the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies will collide in space.
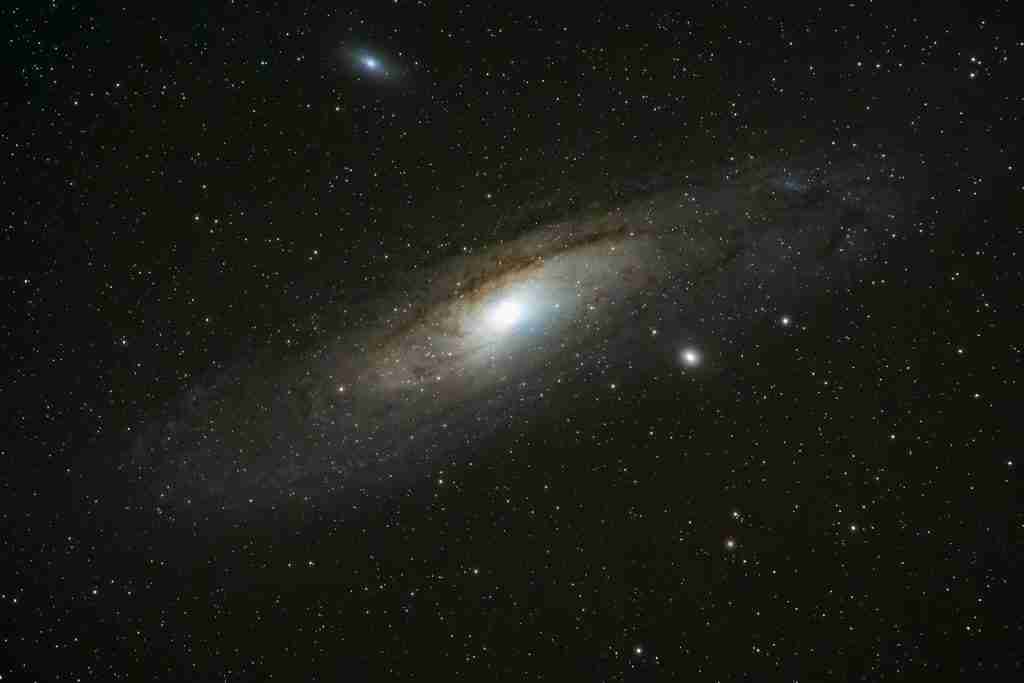

In about 4 billion years, the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies are set to collide, an event-driven by gravity’s pull. This cosmic encounter, taking hundreds of millions of years to complete, will likely move our sun to a new region of the galaxy.
However, scientists say that Earth and our solar system are expected to remain safe throughout this monumental galactic merger.
13. The largest known asteroid in space is 965 km (600 mi) wide.
Ceres, the largest known asteroid with a diameter of 965 kilometers (600 miles), orbits the sun in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
Discovered by G. Piazzi on January 1, 1801, Ceres makes up over one-third of the total mass of all asteroids, roughly one-quarter the size of the Moon, highlighting its significance in our solar system’s asteroid population.
14. The boundary of the solar system is known as the Oort cloud.
The Oort Cloud, a vast spherical shell surrounding our solar system, marks its boundary. This immense region, filled with icy debris ranging from mountain-sized objects to larger ones, potentially holds billions or trillions of celestial bodies.
Beyond it lies interstellar space, a realm within our galaxy not occupied by stars or planets but filled with cosmic rays, gas, and dust.
15. There is a planet made entirely of diamonds in space, called 55 Cancri e.
55 Cancri e, discovered in 2004 and located 40 light-years away in the Cancer constellation, is a diamond planet worth 26.9 nonillion dollars. Orbiting its star every 18 hours, it’s tidally locked, with one side always facing the star and the other in darkness.
Despite its molten surface making it uninhabitable, it presents a fascinating aspect of cosmic discoveries.
16. The International Space Station (ISS) is about as wide as a soccer field.
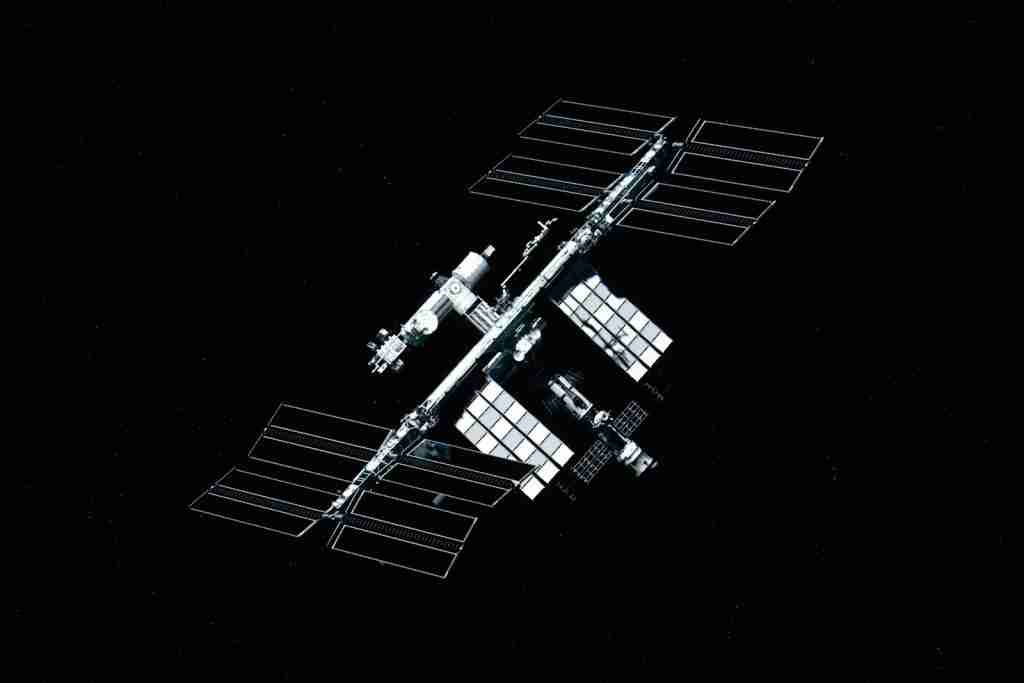

The International Space Station (ISS), with its completion, spans approximately 109 meters by 74 meters, making it slightly larger than a soccer field. Weighing around 420,000 kilograms, equivalent to over 330 cars, its size is comparable to an American football field including the end zones.
This massive structure orbits Earth, serving as a hub for international space exploration and research.
17. Space contains a cosmic neutrino background.
Another interesting fact about space is the existence of the cosmic neutrino background, a sea of low-energy neutrinos that fills the universe. These relic neutrinos, remnants from one second after the Big Bang, now drift through space at a chilly 1.95 K.
With an astonishing density of 336 neutrinos per cm³, they rarely interact with matter, making them elusive cosmic messengers.
18. Do astronauts get taller in space?
Astronauts experience a height increase of up to 3% in microgravity, as observed by NASA. This phenomenon is due to the body’s adaptation to the weightless environment of space.
The change typically happens within the first few days of reaching space, meaning a 6-foot-tall individual could gain up to 2 inches in height during their stay in orbit.
19. If two same types of metal touch in space, they will permanently bond.
One of the mind-blowing facts about space is the phenomenon of cold welding, where two pieces of the same type of metal will permanently bond if they touch in the vacuum of space.
This happens because, without air or moisture, the metal atoms share electrons and fuse, assuming their surfaces are clean and free of oxides or impurities.
20. Massive stars end their lives through supernova explosions in space.
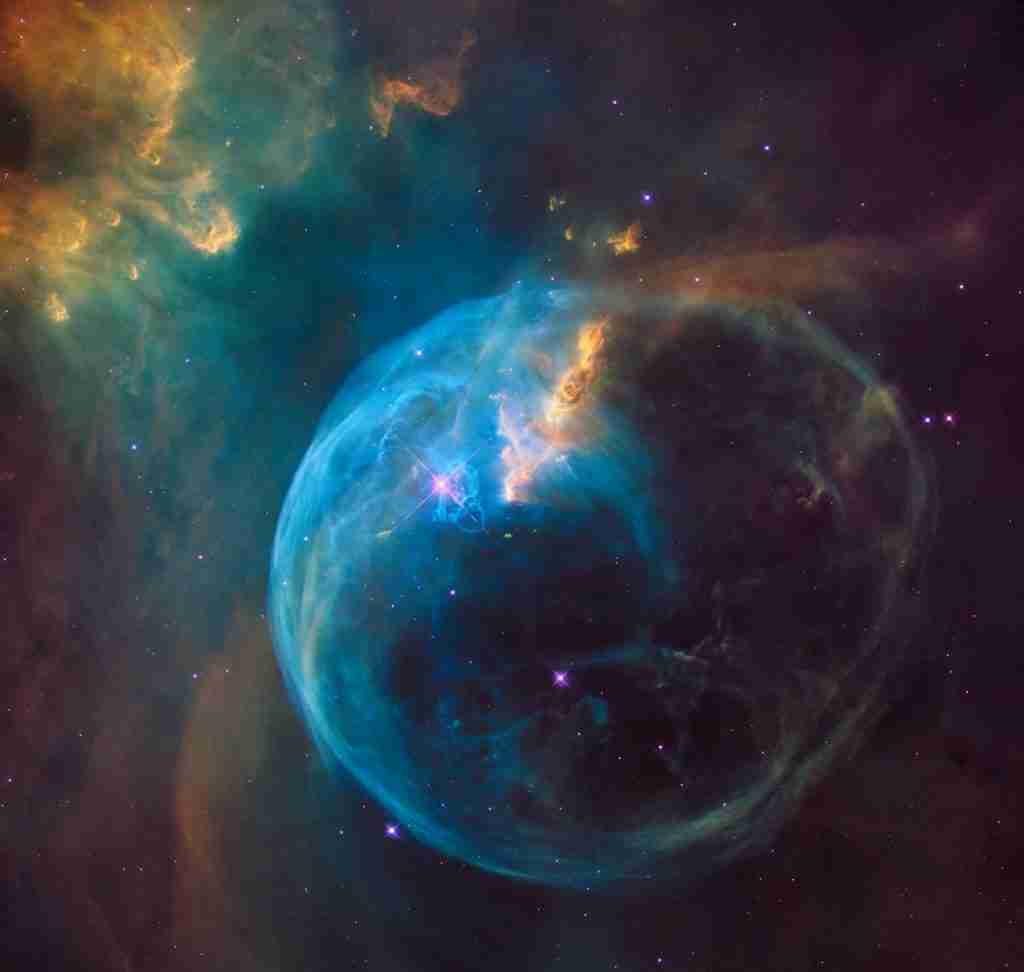

Massive stars conclude their existence with a dramatic event known as a supernova, a powerful explosion that occurs when gravity overtakes the star’s internal pressure, causing it to collapse.
This process not only disperses new atomic nuclei but also forms a glowing remnant. Stars between nine and 50 solar masses may end this way, while larger stars might collapse directly into black holes
21. A rose was brought to space in 1998 to see if it would yield new scents.
In 1998, the ‘Overnight Scentsation’ rose was sent to space aboard the shuttle Discovery, leading to an intriguing discovery. In low gravity, it produced a new, more floral scent, different from its Earth-grown counterpart.
This scent was later used in Shiseido’s Zen perfume and Unilever’s Impulse body spray, showcasing how space can alter a flower’s fragrance.
22. Space between galaxies is still expanding due to the Big Bang.
The space between galaxies is continuously expanding, a momentum originating from the Big Bang, further accelerated by dark energy. While galaxies, stars, and planets remain unchanged in size, the expanding universe carries galaxies apart.
This expansion means we observe galaxies moving away from us in every direction, illustrating the universe’s constant, accelerating growth.
FAQs
In space, without Earth’s atmosphere to obstruct the view, stars can be seen clearly. The absence of atmospheric scattering allows stars to shine more brightly, offering a spectacular view of the cosmos with countless stars visible.
Time cannot exist without space, according to our current understanding of physics. Both are fundamentally linked in the fabric of the universe, known as spacetime, where space provides the context for events to occur in time.
Space is dark because it is mostly empty, lacking surfaces to reflect light. Light travels through space until it hits an object or is absorbed. Without enough nearby light sources, vast areas of space appear dark.
The International Space Station (ISS) is a habitable artificial satellite that orbits Earth. It serves as a space environment research laboratory where scientific research is conducted in astrobiology, astronomy, meteorology, physics, and other fields by international crews.
Space-time curvature is a fundamental idea in Einstein’s theory of general relativity, explaining how gravity is not a force between masses but rather the effect of masses curving space-time, which objects then move through, leading to what we observe as gravitational attraction.








