23 Fun Facts About Mars | Cosmic Surprises
1. Mars has the tallest volcano in the solar system.
Olympus Mons, a shield volcano on Mars, stands at a staggering height of 13.6 miles (22 km). This makes it about three times taller than Earth’s Mount Everest!
The sheer size of Olympus Mons hints at the powerful volcanic forces that shaped Mars in the past. This geological wonder offers clues about the planet’s interior processes.
2. Mars experiences massive dust storms that can engulf the entire planet.
These global storms can last for months, obscuring surface features. They are caused by strong winds kicking up fine dust particles into the Martian atmosphere.
Dust storms on Mars are a reminder of the planet’s active weather patterns. They highlight the challenges for future Mars exploration, both robotic and human.
3. Mars has two small moons, Phobos and Deimos.
These irregularly-shaped moons are thought to be captured asteroids. Mars’s weak gravity was likely unable to form moons through the same process that formed Earth’s Moon.
Phobos and Deimos add to Mars’s visual intrigue. Their unique origin story offers insights into the dynamics of the early solar system.
4. Sunsets on Mars appear blue.
Fine dust in the Martian atmosphere scatters light differently than on Earth, causing a blue tint around the setting Sun. This offers a strikingly different sky spectacle compared to the familiar sunsets we experience.
This twist on a familiar phenomenon adds a touch of the exotic to Mars fun facts. It emphasizes that planets offer their own unique visual experiences.
5. Mars appears reddish due to iron oxide in its soil.
Iron oxide, also known as rust, is abundant on the Martian surface, giving the planet its distinctive color. This rusty hue makes Mars easily recognizable in the night sky.
The iconic red color of Mars is a result of a chemical reaction that occurred over billions of years. It serves as a visual reminder of the planet’s unique composition.
6. Scientists believe that Mars once had liquid water on its surface.
Features like dry riverbeds, canyons, and mineral evidence suggest that Mars had a wetter, warmer past. The search for signs of ancient life on Mars is a driving force behind many missions.
The potential for ancient water on Mars holds fascinating implications for the possibility of past microbial life. It fuels the exciting question of whether Earth is the only planet that has ever hosted life.
7. Mars has polar ice caps that change with the seasons.
The Martian ice caps are composed of water ice and frozen carbon dioxide (dry ice). Their size grows and shrinks depending on the planet’s tilt and its position in its orbit around the Sun.
These dynamic ice caps showcase seasonal changes on Mars, similar to Earth. They also offer a potential source of water for future explorers or even colonies.
8. Mars is home to Valles Marineris, the largest canyon system in the solar system.
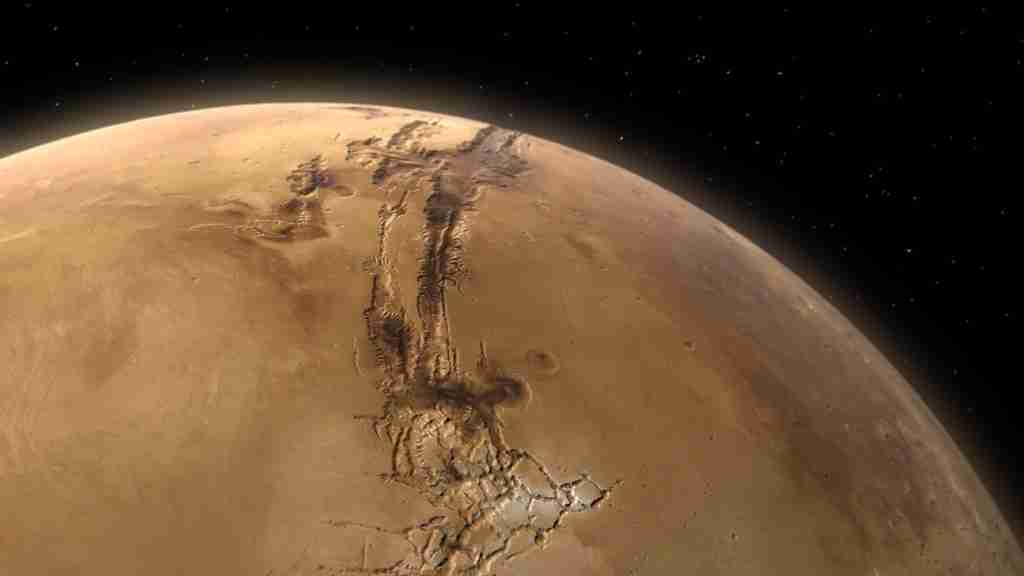
This massive canyon system stretches for about 2,500 miles, dwarfing Earth’s Grand Canyon in scale. Valles Marineris likely formed due to tectonic forces early in Mars’s history.
This geological feature underscores the dramatic landscapes found on Mars. It offers insights into the powerful geological processes that shaped the Red Planet.
9. Humans have sent numerous rovers and landers to explore Mars, uncovering fun facts about Mars with each mission.
Space agencies worldwide have launched successful missions to the Martian surface. These robotic explorers send back valuable images and data, greatly expanding our knowledge of Mars.
This sustained exploration effort demonstrates the scientific fascination with Mars. It highlights the ingenuity and technological advancements that enable us to remotely study another world.
10. Mars has significantly less gravity than Earth.
If you weighed 100 pounds on Earth, you would weigh only about 38 pounds on Mars. This weaker gravity has implications for how objects and potential astronauts would move on the Martian surface.
Mars’s weaker gravity presents both challenges and interesting possibilities for future explorers. It would create a unique physical environment to adapt to and study.
11. A day on Mars is slightly longer than a day on Earth.
A Martian day, called a “sol,” lasts about 24 hours and 37 minutes. This slight difference means explorers or future colonists would need to adapt to a somewhat longer daily cycle on Mars.
The similarity in daytime length offers a familiar anchor point amidst the many differences between Earth and Mars. Despite this similarity, timekeeping on Mars would present adjustments.
12. Mars has the second-largest canyon in the solar system.
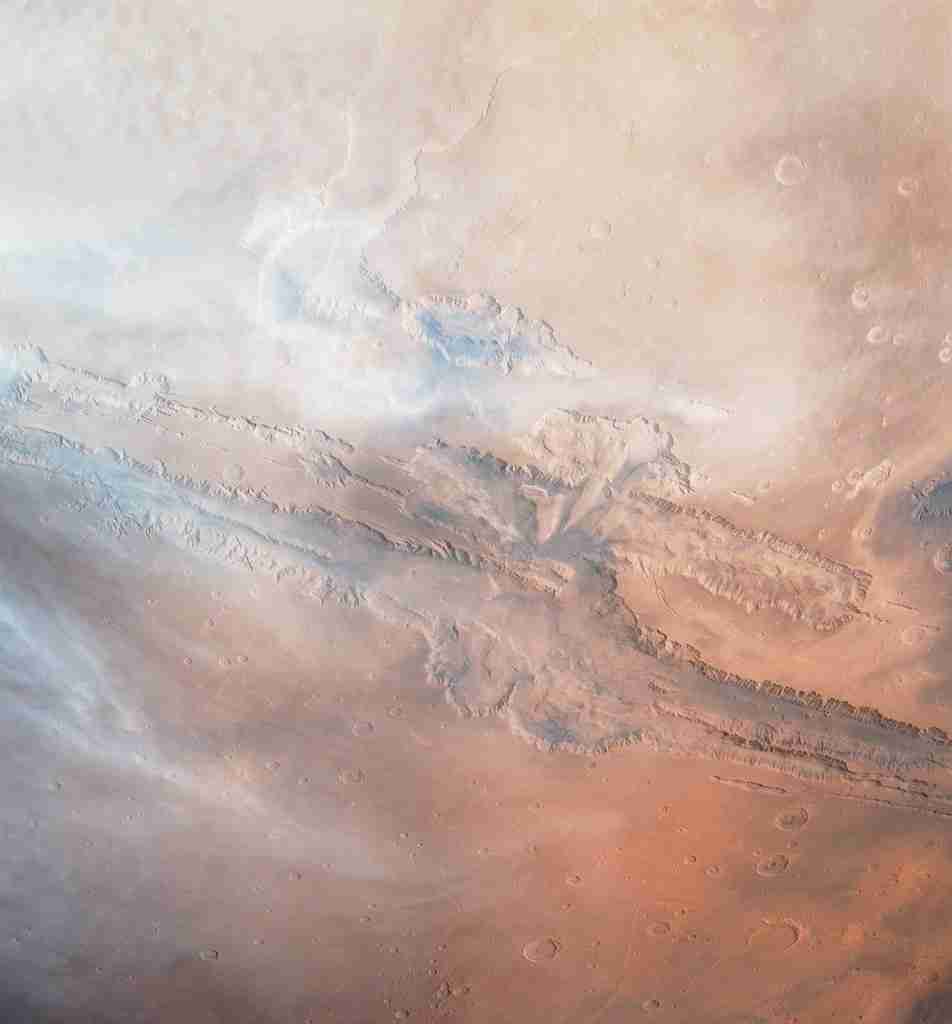

Mars is home to the vast canyon system, Valles Marineris. Its size dwarfs Earth’s Grand Canyon and highlights the Martian landscape’s grand scale.
Valles Marineris showcases fascinating and powerful geological forces that shaped Mars. It’s a visually stunning reminder of the planetary extremes found in our solar system.
13. Mars experiences intense radiation levels.
Lacking a global magnetic field and having a thin atmosphere, Mars is bombarded with high levels of radiation from the Sun and space. This radiation poses a significant risk to any potential life on the surface and future human missions.
Understanding Mars’s radiation environment is crucial for developing protective technologies. It’s a factor scientists must carefully consider when planning long-term stays on Mars.
14. There’s evidence of potential underground water reservoirs on Mars.
Radar data from spacecraft and other observations suggest the presence of subsurface liquid water on Mars. These reservoirs, if confirmed, hold exciting possibilities for finding past or present life forms.
The potential for underground water is one of the most tantalizing Mars facts. This discovery could revolutionize Mars exploration and the search for extraterrestrial life.
15. Mars was once thought to be home to an advanced alien civilization.
In the 19th and early 20th centuries, some astronomers believed they observed “canals” on Mars, thought to be artificial waterways. These observations sparked widespread public interest in the possibility of intelligent Martians.
Although the canal theory was debunked, it fueled imaginations about life on Mars. This historical example demonstrates the enduring fascination humans have with our neighboring planet.
16. Pieces of Mars have landed on Earth as meteorites.
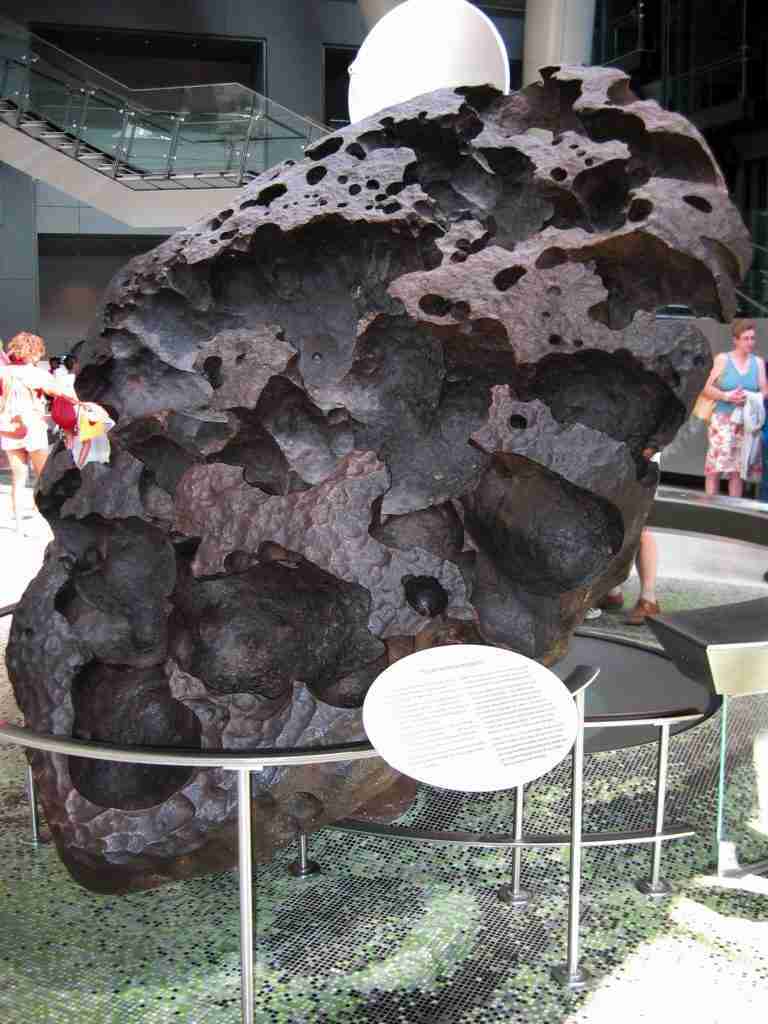

Scientists have identified meteorites found on Earth as having originated from Mars. These rare rocks provide direct samples of Martian geology for analysis.
Martian meteorites offer a unique way to study Mars without having to send spacecraft there. They provide valuable clues about the Red Planet’s composition and history.
17. Mars has its own unique version of auroras.
Unlike Earth’s auroras driven by our magnetic field, Mars experiences a diffuse aurora spread across the planet. This Martian phenomenon is caused by interactions between solar radiation and the planet’s thin atmosphere.
This distinct type of aurora adds another layer to the intriguing atmospheric processes on Mars. It demonstrates the diverse ways planets interact with solar energy.
18. You would weigh much less on Mars than on Earth.
Due to Mars’s lower gravity, you would experience a significant weight reduction if you were to stand on its surface. This change in weight offers a fun and relatable way to understand the differences between the two planets.
Playing with the idea of Martian weight-loss is a lighthearted way to illustrate a scientific concept. It makes the differences in gravity more tangible.
19. Mars has a very thin atmosphere compared to Earth.
The Martian atmosphere is primarily composed of carbon dioxide and is about 100 times thinner than Earth’s atmosphere. This thin atmosphere offers little protection from radiation and makes breathing impossible for humans without specialized suits.
This fact about Mars highlights the challenges of exploration on its surface. It emphasizes the need for technology to overcome the harsh Martian environment.
20. Pieces of Mars may have signs of fossilized life.
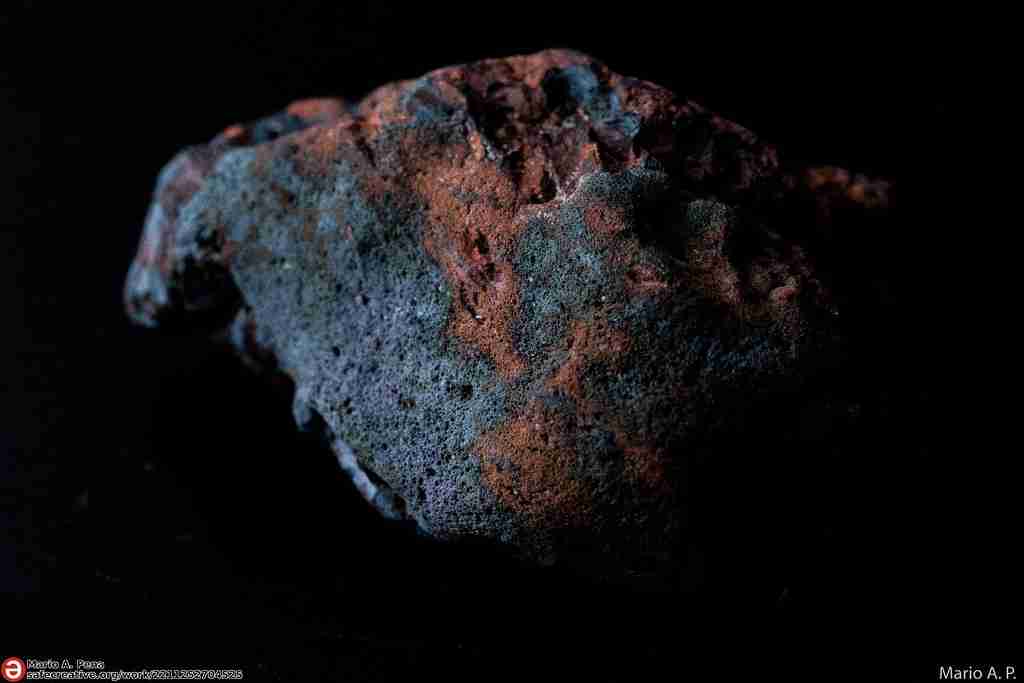
In 1996, a meteorite believed to be from Mars was found to contain potential microscopic fossils of ancient bacteria. While still debated, this discovery raises the fascinating possibility of past life on Mars.
Whether the evidence confirms ancient life or not, it fuels the ongoing search for signs of biology beyond Earth. This exploration holds enormous implications for our understanding of the universe.
21. Mars and Earth experience similar tilt in their rotation axis.
Both Mars and Earth have tilted rotation axes, resulting in the experience of seasons. This shared characteristic offers a connection to our own planet, despite the vast differences between the two worlds.
This similarity hints at potential commonalities in planetary formation and behavior. It allows for comparisons of seasonal changes on Earth and Mars.
22. Mars has the most extreme temperatures in the solar system after Mercury.
Temperatures on Mars can swing wildly, from a potential high of around 70 degrees Fahrenheit to lows of about minus 225 degrees Fahrenheit. This extreme range creates challenges for spacecraft and future human explorers.
These dramatic temperature fluctuations highlight the harsh conditions on the Martian surface. They emphasize the need for specialized technology and suits to withstand such extremes.
23. Some scientists want to terraform Mars.
Terraforming refers to the hypothetical process of transforming Mars into a more Earth-like environment capable of supporting life. Ideas range from releasing greenhouse gases to introducing life forms.
While currently in the realm of science fiction, the concept of terraforming Mars sparks debates about ethics and feasibility. It showcases the potential for human ambition to drastically alter other worlds.
FAQs
The surface of Mars is predominantly rocky, dusty, and barren, characterized by vast deserts, ancient volcanoes, and deep canyons, such as Valles Marineris.
Mars has two moons, Phobos and Deimos, which are irregularly shaped and likely captured asteroids or debris from impacts with other celestial bodies.
The temperature on Mars varies significantly, with average surface temperatures ranging from about -80 degrees Fahrenheit (-62 degrees Celsius) near the poles to around 70 degrees Fahrenheit (20 degrees Celsius) at the equator during the day.
NASA has conducted numerous missions to explore Mars, including robotic rovers like Curiosity and Perseverance, which have provided valuable data about the planet’s geology, atmosphere, and potential for past or present life.
Mars’ atmosphere is primarily composed of carbon dioxide (CO2), with trace amounts of other gases such as nitrogen, argon, and oxygen.







