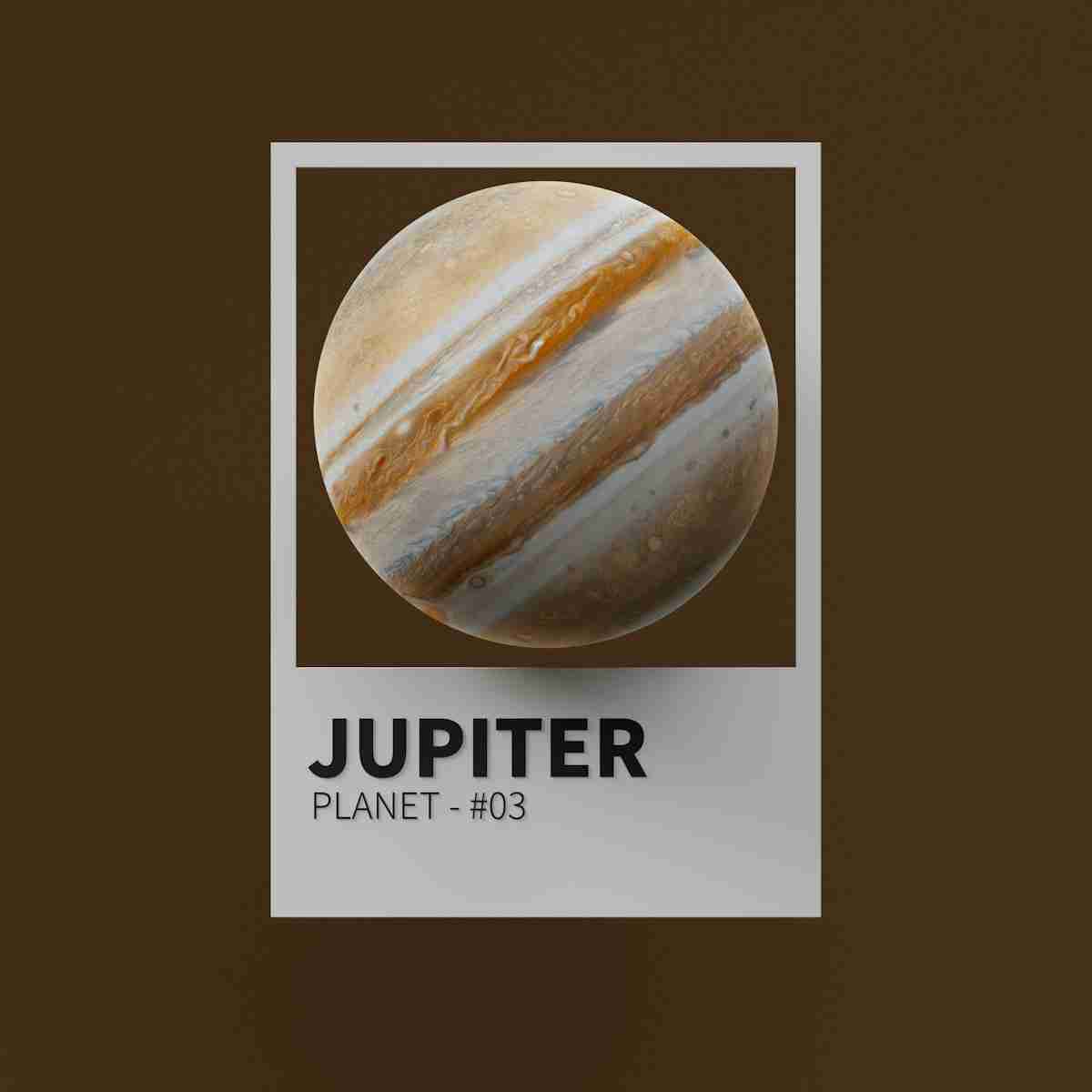
24 Fun Facts About Jupiter | Giant’s Secrets
1. Composed mostly of hydrogen and helium, Jupiter’s makeup is similar to that of stars.
This composition highlights Jupiter’s place in the solar system as a gas giant, bridging the gap between planet and star with its star-like characteristics.
Studying its composition helps scientists learn more about the early solar system and the processes that led to the formation of other celestial bodies.
2. It has the shortest day of all the planets, completing one rotation in just about 9 hours and 55 minutes.
Jupiter’s rapid rotation is a key factor in its meteorological and atmospheric phenomena, contributing to its unique physical features.
This fast spin results in extreme weather patterns that are unlike those on any other planet, making it a subject of endless study and fascination.
3. Lacking significant axial tilt, Jupiter does not experience distinct seasons like Earth.
The absence of seasons on Jupiter provides a unique environment for studying atmospheric stability and dynamics without the complication of seasonal changes.
This constant environment helps scientists focus on other variables affecting the planet’s atmosphere and weather.
4. Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system, capable of fitting 11 Earths side by side across its diameter.
Jupiter stands out as the largest planet in our solar system. When discussing fun facts about Jupiter, its sheer size is a must-mention.
This gas giant’s volume is so vast that it could fit all other planets inside it and still have room to spare. That’s a staggering thought!
5. The planet’s magnetic field is the most powerful in the solar system, significantly stronger than Earth’s.
The magnetic field of Jupiter is another fascinating aspect, extending thousands of kilometers into space and protecting the planet from solar winds.
This immense magnetic influence affects not only Jupiter but also contributes to the safety of its moons, making it a key area of research.
6. Jupiter has been a key target for spacecraft explorations, including the Pioneer, Voyager, and Juno missions.
These missions have provided a wealth of data about Jupiter, making it one of the most studied planets in our solar system.
The insights gained from these explorations continue to inform our understanding of the giant planet and its complex system.
7. The core temperature of Jupiter may exceed 36,000 degrees Celsius, hotter than the surface of the sun.
This extreme core temperature underpins the intense internal processes occurring within Jupiter, driving many of its surface phenomena.
Understanding these conditions provides insights into planetary formation and the behavior of gas giants under different cosmic conditions.
8. With 92 known moons, Jupiter’s largest moon, Ganymede, is bigger than Mercury.
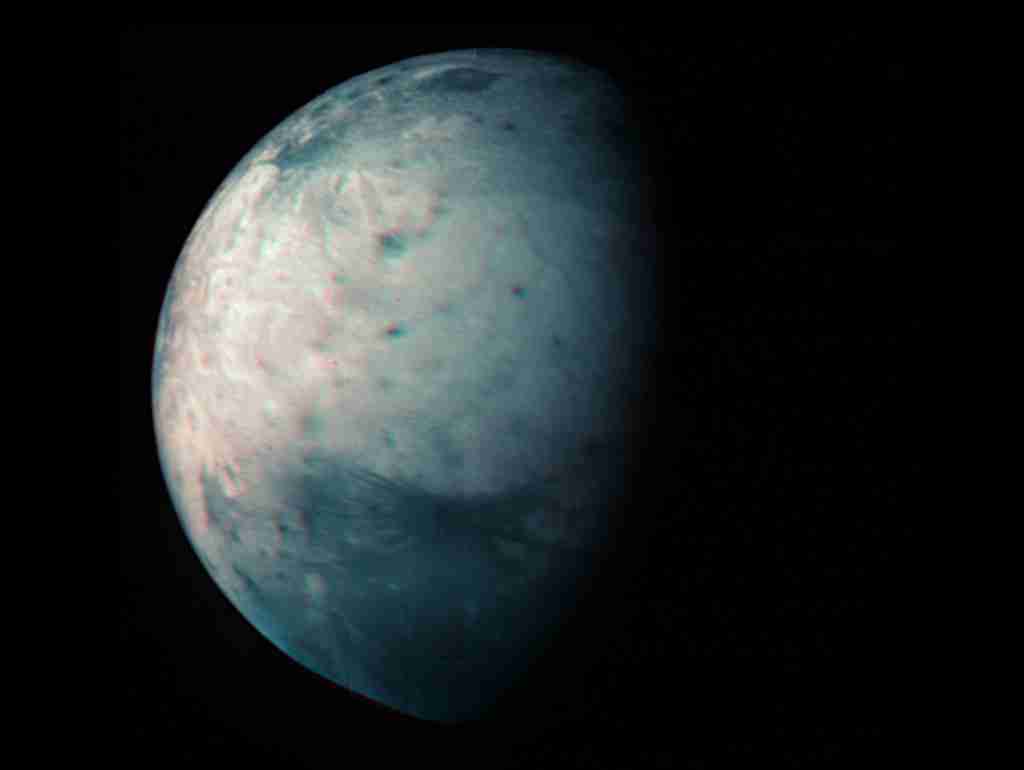
This fact about Jupiter’s moons highlights the diversity and richness of the objects orbiting the gas giant, each with its own unique characteristics and mysteries.
Ganymede’s size and geological features make it an especially interesting subject for scientific study and exploration.
9. Jupiter’s faint rings were discovered in 1979 and continue to be studied for their unique properties.
While not as visually striking as Saturn’s, the rings of Jupiter add to the complex and intriguing nature of this gas giant.
These rings challenge our understanding of ring systems and hint at dynamic processes involving Jupiter’s moons and possibly captured debris.
10. The planet’s immense gravity helps protect Earth by diverting potentially hazardous comets and asteroids.
This protective aspect of Jupiter is a vital part of the solar system’s safety mechanism, shielding Earth from many potential impacts.
Its gravitational influence acts as a cosmic shield, making Jupiter a crucial player in the stability of the solar system.
11. Jupiter’s rapid rotation causes its equatorial region to bulge and poles to flatten.
This distinct rotational characteristic influences everything from Jupiter’s wind patterns to its magnetic field.
The planet’s unusual shape due to its rotation offers a perfect example of the physical consequences of rapid spinning in the cosmos.
12. The Great Red Spot on Jupiter is a massive storm larger than Earth that has been raging for over 300 years.
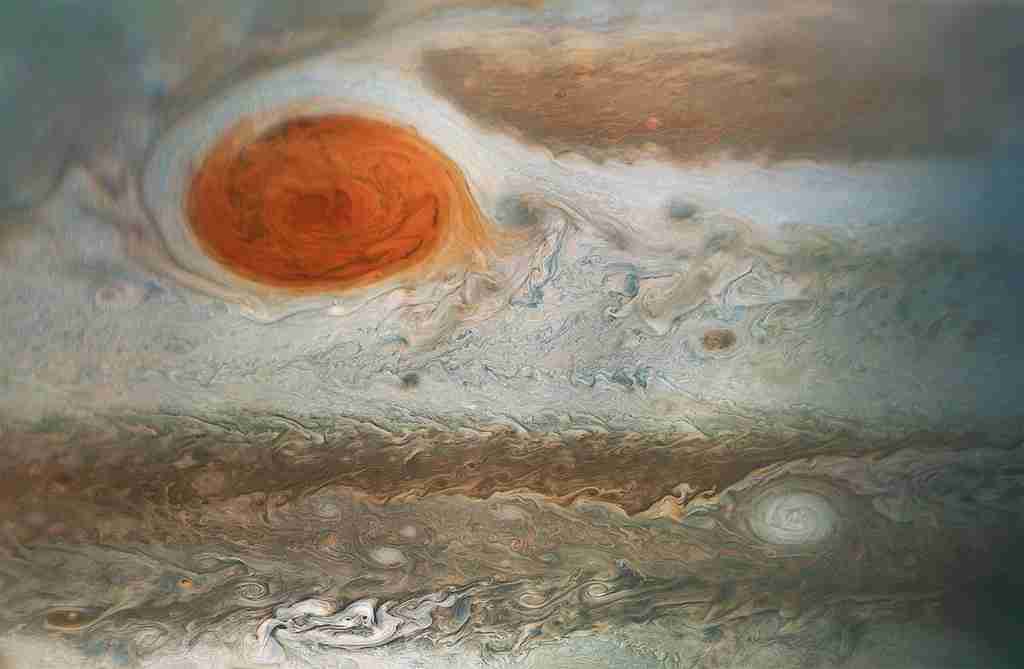

This enduring storm is one of the most captivating Jupiter fun facts, offering a glimpse into the dynamic and tumultuous atmosphere of the gas giant.
The Great Red Spot’s persistence and size provide crucial clues to understanding Jupiter’s atmospheric dynamics and longevity.
13. If it were about 80 times more massive, Jupiter could have become a star due to nuclear fusion in its core.
This intriguing scenario highlights the thin line between planet and star, as Jupiter teeters on the edge of what could have been stellar status.
The theoretical transformation into a star showcases the dynamic nature of celestial bodies and the fascinating what-ifs of astronomy, further enriching the collection of facts about Jupiter.
14. The atmosphere of Jupiter features multiple cloud layers.
Jupiter’s atmosphere is not only vast but vibrant, with colorful bands and intense auroras that illuminate its poles, making this a prime example of Jupiter facts that capture our imagination.
These energetic auroras are a result of the planet’s powerful magnetic field, offering a spectacular light show that is unrivaled by any other planet in our solar system.
15. Jupiter’s magnetic field is about 20,000 times stronger than Earth’s.
This immense strength makes Jupiter’s magnetic field a formidable force, extending far beyond the planet itself and influencing its environment and moons.
The magnetic field is so strong that it creates a magnetosphere large enough to contain the sun, were it placed at the center.
16. Jupiter’s auroras are the brightest in the solar system, displaying stunning light shows.

The brightness and visibility of Jupiter’s auroras make them a fascinating subject for both astronomers and enthusiasts, providing a cosmic spectacle that’s vividly visible with modern space telescopes.
These auroras contribute to the array of fun facts about Jupiter, showcasing the dynamic interactions between the solar winds and Jupiter’s magnetic field.
17. It’s so large that more than 1,300 Earths could fit inside Jupiter.
This fact highlights Jupiter’s immense volume, providing a perspective on its scale and the sheer size that defines this giant planet.
Such comparisons help us appreciate the massive scale of objects in our solar system and their gravitational pull.
18. Jupiter has a powerful influence on the solar system and can alter the orbits of other planets.
Known as the solar system’s vacuum cleaner, Jupiter’s gravitational pull is so strong that it has influenced the paths of comets and other bodies, effectively shaping the orbital dynamics of our solar system.
This gravitational force can even capture interstellar objects or throw them out of the solar system, demonstrating Jupiter’s role as a guardian and sculptor of our cosmic neighborhood.
19. It has the fastest rotation speed of any planet in the solar system.
Jupiter’s rapid rotation contributes significantly to its unique geophysical and atmospheric phenomena, such as its extreme winds and the flattening at its poles.
This quick rotational period is key to understanding how Jupiter’s magnetic field and weather patterns are so drastically different from those of Earth.
20. The planet’s rings are made primarily of dust particles.
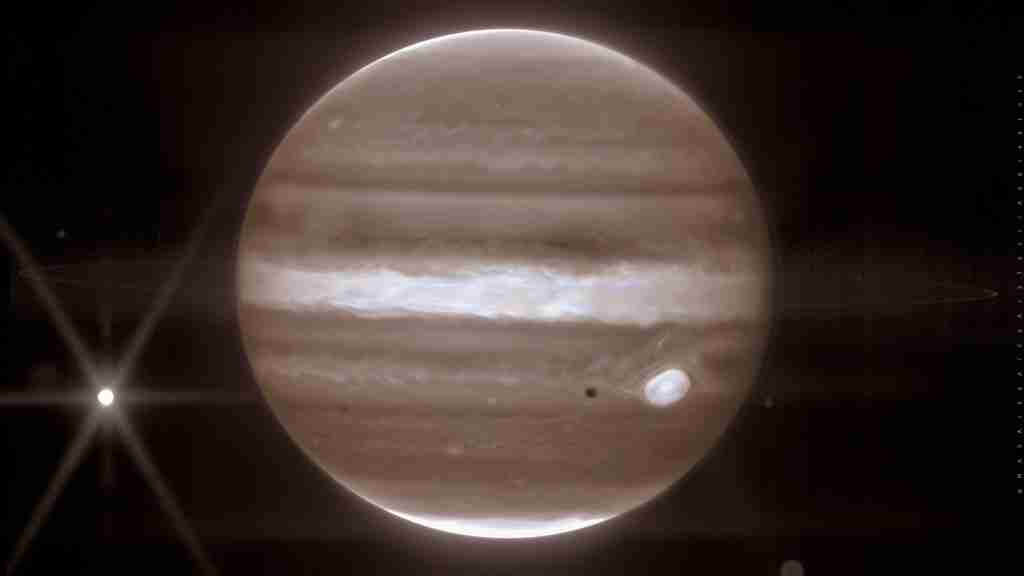

Unlike the icy rings of Saturn, Jupiter’s rings are composed mostly of fine dust, which is believed to be produced by micrometeoroid impacts on its moons.
This composition provides clues to the processes that occur in less dense but equally fascinating ring systems around planets.
21. Jupiter’s atmosphere transitions from gaseous to liquid due to the immense pressure.
Deep within Jupiter, the pressure is so high that gases turn into liquids, leading to a fluid mixture of hydrogen and helium beneath the cloud tops.
This transition provides insight into the internal structure and composition of Jupiter, highlighting the extreme conditions that prevail inside this gas giant.
22. The planet’s interior may contain a core of rocky material heavier than Earth.
The existence of a dense core within Jupiter suggests that it may hold more secrets about the early solar system’s formation processes.
Understanding whether Jupiter has a solid core influences how scientists model the formation of other gas giants both in our solar system and in exoplanetary systems.
23. Jupiter emits more heat than it receives from the Sun.
Jupiter’s ability to emit more heat than it receives is due to its residual heat from its own formation, illustrating its role as a mini heat source within our solar system.
This excess heat affects the thermal structure of the planet and drives much of its atmospheric activity, including its vast storms and jet streams.
24. The planet has a strong effect on asteroid belts.

By acting as a gravitational shield, Jupiter not only protects Earth but also influences the stability and structure of the asteroid belt, keeping the inner solar system relatively free of potential impacts.
This protective aspect is crucial in maintaining life on Earth as we know it, showcasing Jupiter’s indispensable role in our solar system.
FAQs
Jupiter has 92 confirmed moons, the highest number in our solar system.
Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system, renowned for its enormous size, strong magnetic field, and the iconic Great Red Spot.
NASA’s missions, such as the Galileo orbiter and the ongoing Juno mission, have explored Jupiter’s atmosphere, magnetic field, and structural composition.
Some of Jupiter’s most famous moons include Ganymede, Callisto, Io, and Europa, with Ganymede being the largest moon in the solar system.