28 Fun Facts About Romans | Ancient Insights
1. Romans used symbols like I, V, X, L, C, D, and M for their numbering system.
The Roman numerical system employed symbols like I, V, X, L, C, D, and M for representing numbers, forming the basis for modern numeral systems.
This system is still influential and used in various contexts today.
2. According to legend, Rome was founded by Romulus and Remus.
Legend attributes the founding of Rome to Romulus and Remus, twin brothers raised by a she-wolf, whose rivalry led to the establishment of the city.
This mythological tale is foundational to the identity of Rome.
3. The Roman Empire spanned Europe, Africa, and Asia, making it one of history’s largest.
At its zenith, the Roman Empire was one of the largest in history, covering vast regions across Europe, Africa, and Asia.
Its influence shaped the course of Western civilization.
4. Roman roads were advanced and enduring, with some still in use.
The Romans constructed a sophisticated network of roads, known for their advanced engineering, and some of these ancient roads are still in use today.
Their road system facilitated communication and trade across the empire.
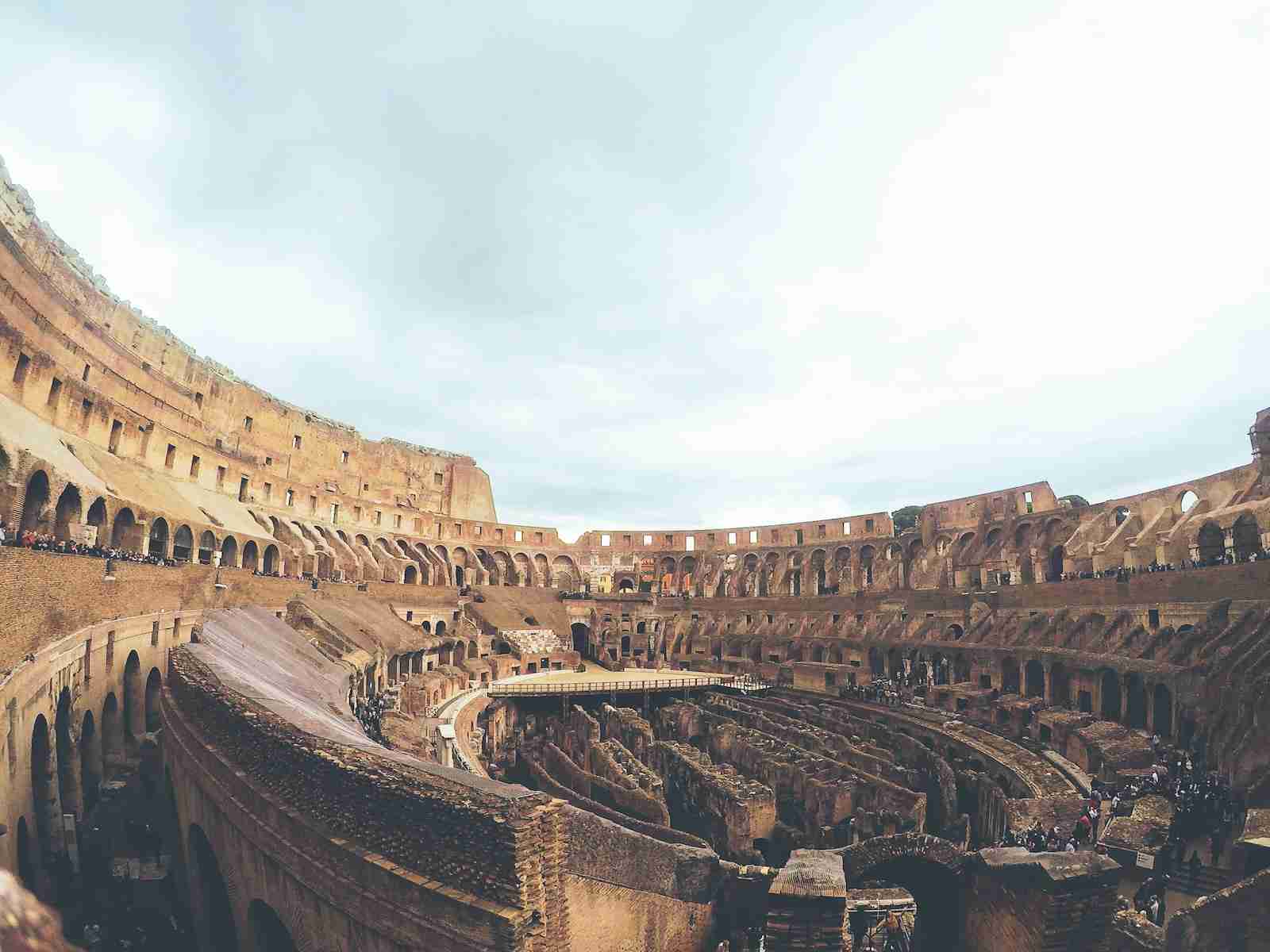
5. Rome’s Colosseum could host 50,000 spectators for gladiator fights and events.
The Colosseum in Rome, an iconic amphitheater, could accommodate up to 50,000 spectators, hosting events like gladiator fights and mock sea battles.
This architectural marvel remains an enduring symbol of Roman entertainment.
6. Latin, Rome’s language, is the root of many modern languages.
Latin, the language of ancient Rome, serves as the root for many modern languages, particularly the Romance languages like Italian, Spanish, French, and Portuguese.
Its legacy persists in legal, scientific, and religious contexts.
7. The Romans invented concrete, changing architectural possibilities.
The Romans revolutionized construction by inventing concrete, a pivotal development that transformed architectural possibilities and contributed to the longevity of their structures.
This innovation laid the foundation for future construction techniques.
8. Julius Caesar was a key figure in the rise of the Roman Empire.
Julius Caesar played a pivotal role in the rise of the Roman Empire, his military conquests and political maneuvers significantly influenced Roman history.
His leadership marked a crucial turning point in the republic’s transition to an empire.
9. Roman baths were centers for bathing, socializing, and business.
Roman baths served as multifunctional centers where people engaged in bathing, socializing, and even business transactions, reflecting the communal aspects of Roman society.
These spaces were integral to daily life and cultural practices.
10. The Roman calendar preceded today’s Gregorian calendar.
The Roman calendar, reformed by Julius Caesar and refined by Augustus Caesar, preceded the Gregorian calendar we use today, influencing the organization of time globally.
It reflected the Romans’ understanding of astronomical cycles and religious observances.
11. Roman law greatly influenced modern legal systems, which is one of the fun facts about Romans.
Roman law, with its foundational principles and legal concepts, had a profound impact on the development of modern legal systems.
Concepts like “innocent until proven guilty” and legal rights originated from Roman jurisprudence.
12. Romans built impressive aqueducts for water transport.
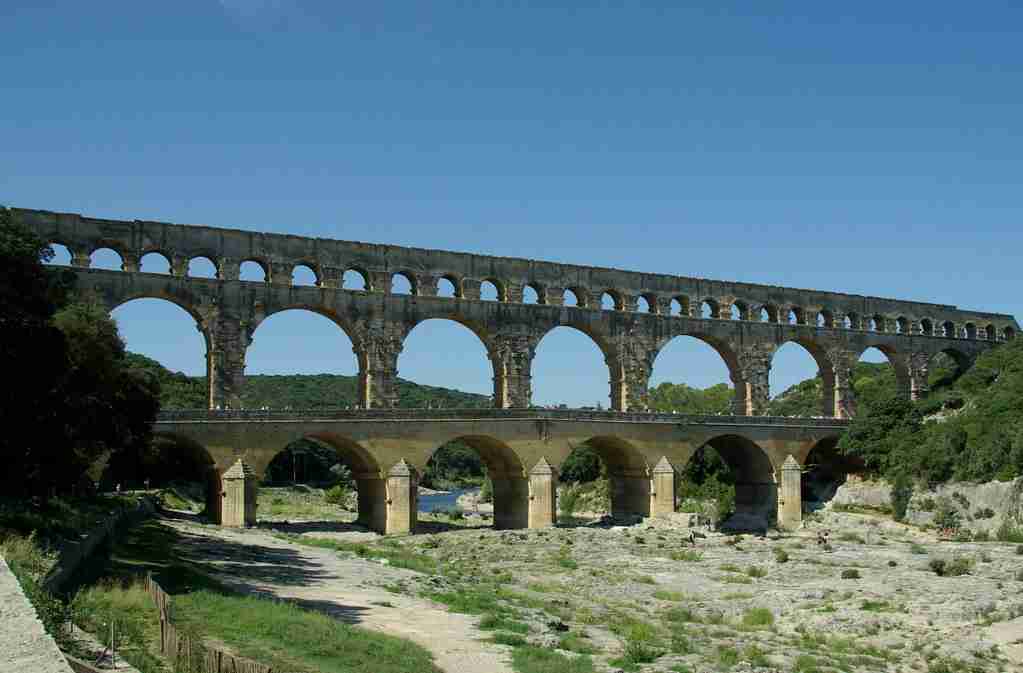

The Romans engineered impressive aqueducts to transport water over long distances, contributing to urban development and ensuring a reliable water supply for cities.
These feats of engineering showcased their mastery of water management.
13. Roman cuisine included bread, olives, and wine.
Roman cuisine featured staples such as bread, olives, and wine, forming the foundation of their diet and cultural practices.
These elements represented both sustenance and symbols of social and religious significance.
14. Romans used a sponge on a stick as toilet paper.
In ancient Rome, hygiene involved the use of a sponge attached to a stick as a form of rudimentary toilet paper in communal latrines.
This practice reflects aspects of daily life and sanitation in ancient Roman society.
15. Romans were known for elaborate festivals and entertainment.
Romans were avid celebrants, organizing elaborate festivals and diverse forms of entertainment to mark various occasions.
These festivities included theatrical performances, chariot races, gladiator contests, and religious celebrations, contributing to the cultural richness of Roman society.
16. Togas, mainly worn by men, were popular in Rome.
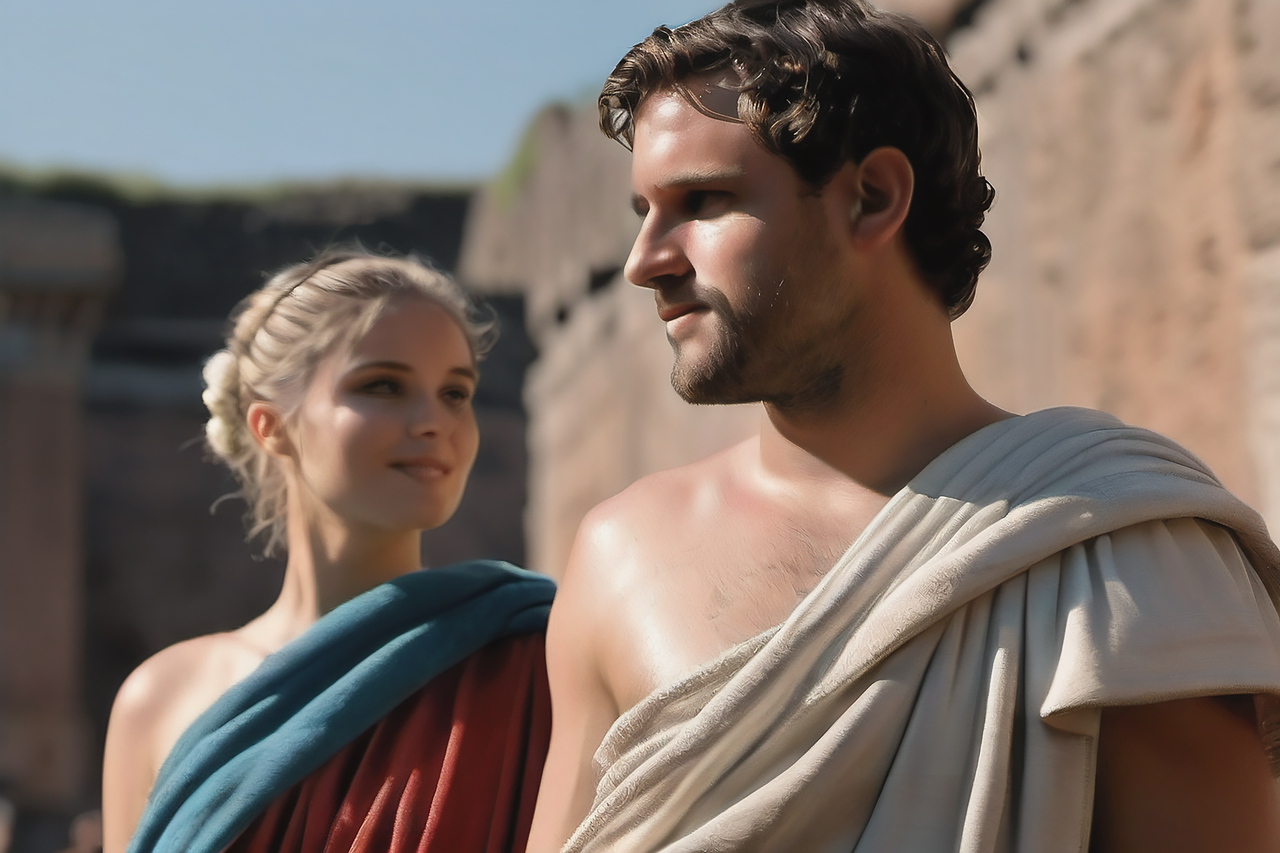

Togas, distinctive Roman garments, were predominantly worn by men and symbolized Roman citizenship and status.
They were worn for various formal occasions, embodying Roman identity and social hierarchy.
17. Chariot racing was a favorite Roman sport.
Chariot racing, a thrilling and popular sport in ancient Rome, was conducted in large arenas like the Circus Maximus, attracting massive crowds and fervent enthusiasm.
It became an integral part of Roman entertainment culture.
18. Romans worshipped a pantheon of gods and goddesses.
Romans embraced a diverse religious belief system and worshipped a pantheon of gods and goddesses, each associated with specific aspects of life and nature.
Religious practices played a crucial role in Roman daily life and societal norms.
19. Pax Romana was a period of peace in the Roman Empire.
Pax Romana, a relatively stable and peaceful period, characterized the Roman Empire from 27 BCE to 180 CE.
During this time, the empire experienced minimal military conflict, fostering prosperity and cultural development.
20. The Romans used hypocausts for heating baths and houses.
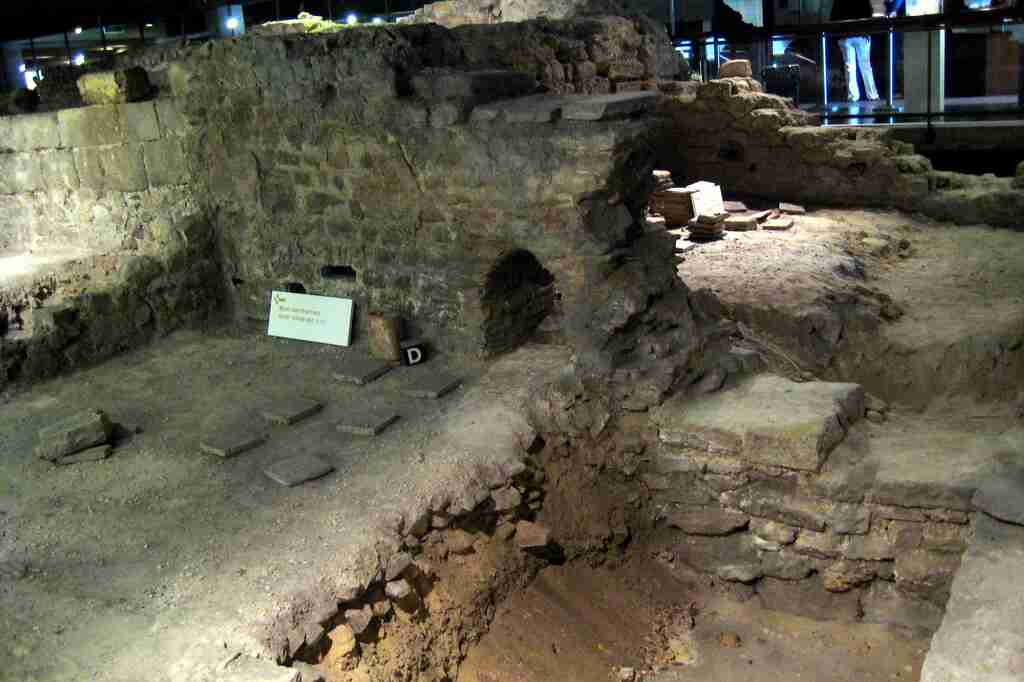

Romans implemented hypocausts, an early form of underfloor heating, to warm their baths and homes, showcasing their innovative approach to comfort and technology.
This heating system circulates hot air beneath floors, providing efficient warmth.
21. Roman women had more rights than in many ancient societies.
Compared to some contemporary societies, Roman women had relatively more rights and legal status, including the ability to own property and engage in business transactions.
While not equal to men, these rights were notable in the ancient world.
22. The Roman Empire’s fall in 476 AD began the Middle Ages.
The fall of the Roman Empire in 476 AD marked the end of ancient times and the beginning of the Middle Ages, a period characterized by significant social, political, and cultural changes.
This transition had profound and lasting impacts on European history.
23. Romans had a complex government with checks and balances.
The Roman Republic had a complex system of government that included checks and balances, with various branches and offices to prevent the concentration of power.
This political structure influenced later democratic systems.
24. Romans left a legacy of monuments, roads, and cities.
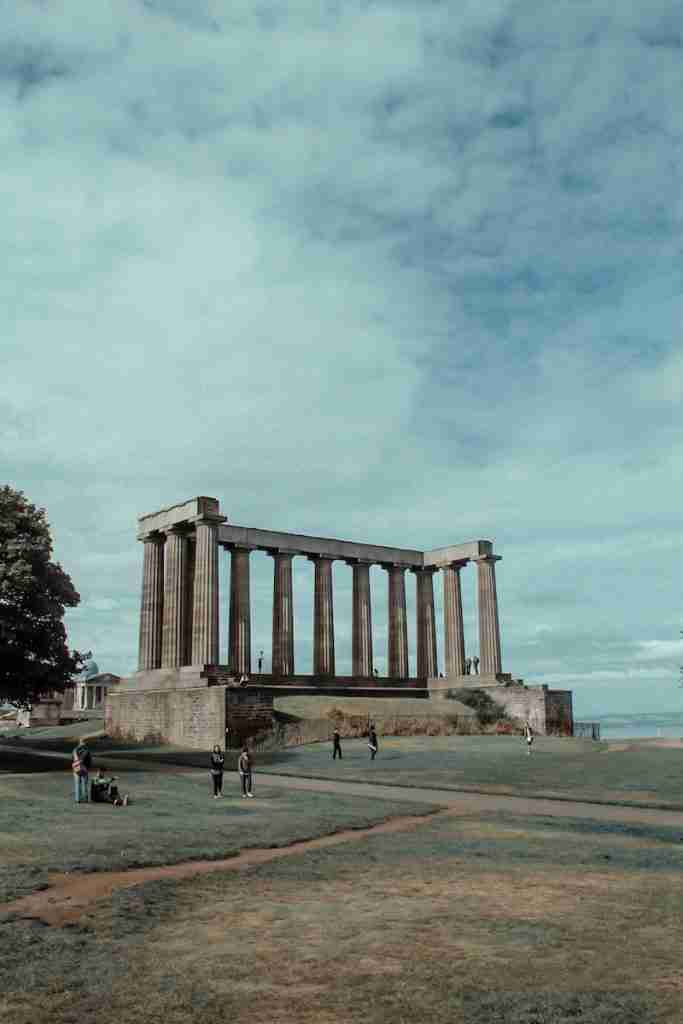

The Romans left an enduring legacy of monumental architecture, extensive road networks, and well-planned cities that still stand as testaments to their engineering and organizational prowess.
These structures continue to be studied and admired today.
25. Ancient Rome peaked at about 1 million inhabitants.
At its height, ancient Rome boasted a population of around 1 million inhabitants, making it one of the largest and most densely populated cities in the ancient world.
This demographic size contributed to the complexity and vibrancy of Roman society.
26. What is the meaning of Romans 8:28?
Romans 8:28 states, “And we know that in all things God works for the good of those who love him, who have been called according to his purpose.” It emphasizes God’s purpose in all circumstances.
27. Roman education emphasized literature, rhetoric, and philosophy.
Roman education focused on the study of literature, rhetoric, and philosophy, with an emphasis on producing well-rounded individuals capable of intellectual and civic engagement.
This educational approach influenced the development of classical scholarship.
28. The Roman army was disciplined, organized, and innovative.
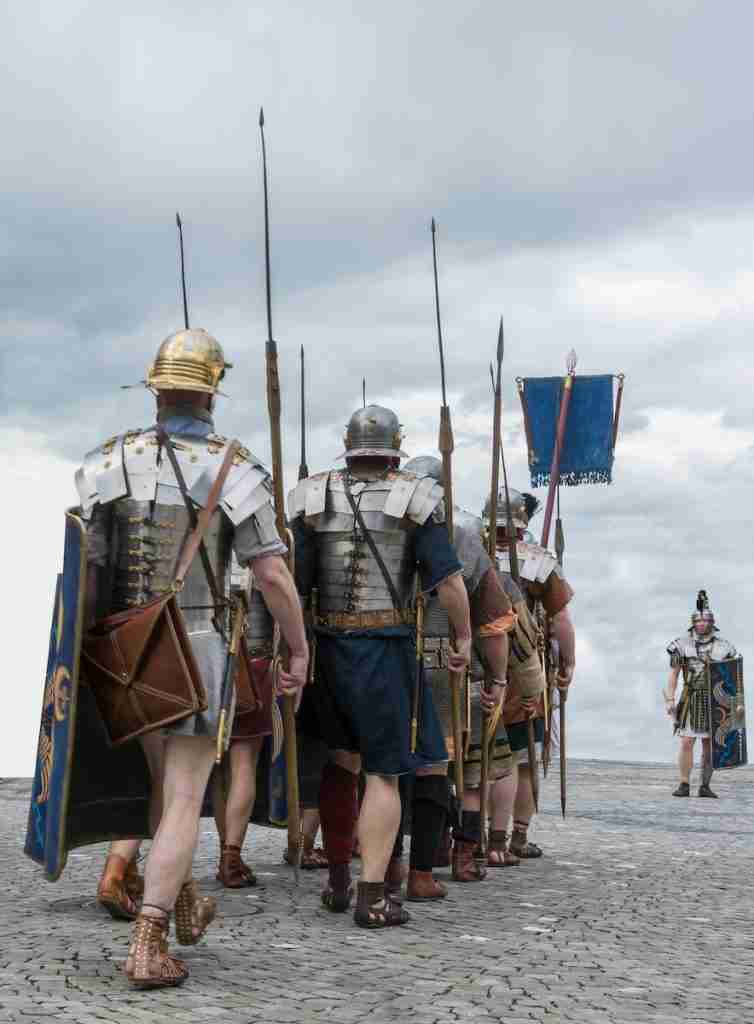

The Roman army, renowned for its discipline, organization, and innovative military tactics, played a critical role in the expansion and defense of the empire.
These qualities contributed to the longevity and success of Roman military campaigns.
FAQs
Romans 12:1-5 encourages believers to offer themselves as living sacrifices to God, using their unique gifts for the benefit of the Christian community.
Romans 6:6 discusses the crucifixion of the old self, emphasizing the idea that believers are no longer slaves to sin but have a newness of life in Christ.
A commentary on Romans 1 provides insights into the context, themes, and interpretations of the first chapter of the Book of Romans.
Romans VI” could refer to Chapter 6 of the Book of Romans, which discusses the believers’ identification with Christ’s death and resurrection, symbolized through baptism.
Romans 12:22 encourages believers to overcome evil with good, emphasizing the transformative power of love and kindness.