28 Fun Facts About Space Exploration You Never Knew
1. Mariner 2, which passed by Venus in 1962, was the first robotic space probe to successfully conduct a planet-wide encounter.
In 1962, Mariner 2 changed the landscape of outer space exploration. For the first time ever, a spacecraft left our planet to visit another. It’s a fascinating mission. To fly by Venus.
To Rocket scientists everywhere, this journey represents a massive milestone in our understanding and capabilities of reaching the outermost regions of our galaxy. Before this momentous event, planetary exploration existed only in dreams and widespread questions wondered what personal evidence anyone may have of life found outside Earth’s domain.
But with the successful mission by Mariner 2 on December 14th, 1962, humans recognized for the first time that traveling beyond our borders is indeed possible — slowly opening up an entirely new realm of opportunities for better understanding ourselves and our rare place in our universe once reserved as unknown frontiers.
2. The First Spacecraft to land on another planet was Mars 3, which landed on Mars in 1971.
In 1971, history was made when the first ever spacecraft landed on a different planet: Mars 3.
This spacecraft opened the door to interplanetary exploration and set off a race among world powers as they each sought to make their own groundbreaking discoveries beyond our own planetary system.
Since this initial achievement, technologically advanced spacecraft have been created and used to probe more of the universe’s mysteries.
They’ve captured gorgeous photos of planets, punched through their atmospheres with innovative landers and robots, and scanned their surface features up close through rovers and orbiters with cameras, x-ray spectrometers, infrared imagers & cameras, and many other tools.
3. The First spacecraft to orbit another planet was Mars 1, which orbited Mars in 1971.
In 1971, the first ever spacecraft to orbit a planet other than our own was Mars 1.
Breaking boundaries and traversing realms that, up until that point, no manmade object had, it served as an early chapter in the exploration of our solar system.
Never before had so ambitious a mission been conceived and completed successfully; it circled its celestial target from afar with grace and precision.
4. The First spacecraft to fly past Jupiter was Pioneer 10, which flew by in 1973.

Jupiter in 1973.
In 1973, a revolutionary milestone was achieved in space exploration: Pioneer 10 became the first spacecraft to soar past Jupiter. It exhibited a meteoric speed of nearly 110,000 kilometers per hour, allowing it to traverse tens of millions of kilometers between Earth and the Jovian planets in a single day.
While launching from Earth on March 2 of that same year, its primary mission was to study and map the Jovian environment with five scientific experiments as well as audiovisual recordings.
Its journey marked an incredible technological revolution and sparked further ambitious inquisitions in astronomy!
5. The First spacecraft to land on Jupiter’s moon, Europa, was the Galileo spacecraft in 1995.
The historic moment arrived in 1995 when the Galileo spacecraft made history as the first spacecraft to land on Jupiter’s moon, Europa. It was an incredible feat, largely thanks to the dedication of a team of scientists and engineers who worked vigorously toward the success of this project.
A full decade prior Galileo launched into space with an ambitious task to explore the outermost regions of our solar system and gather essential data about distant planets.
Over time it underwent numerous advanced interstellar upgrades which enabled it to speed off towards its ultimate destination: Jupiter’s moon Europa – which offered exemplary potential for research opportunities and new understanding. raft in 1995.
7. The First spacecraft to land on an asteroid was NEAR Shoemaker.
In 2001, history was made when the first spacecraft, known for its “fun facts about space exploration,” touched down on an asteroid. This feat was accomplished through the land of NEAR Shoemaker on Eros– no small task!
This record-breaking mission successfully marked the first time a spacecraft to an asteroid had ever been landed. After eight years of preparation and planning, humankind reached a great milestone as NEAR Shoemaker urged past space dust in order to reach its destination.
In 2021, over 40 different asteroids have been explored and surveyed by previously established spacecraft such as NEAR Shoemaker declaring it one giant proud moment for human innovation.
8. The First spacecraft to land on a comet was the Rosetta spacecraft.
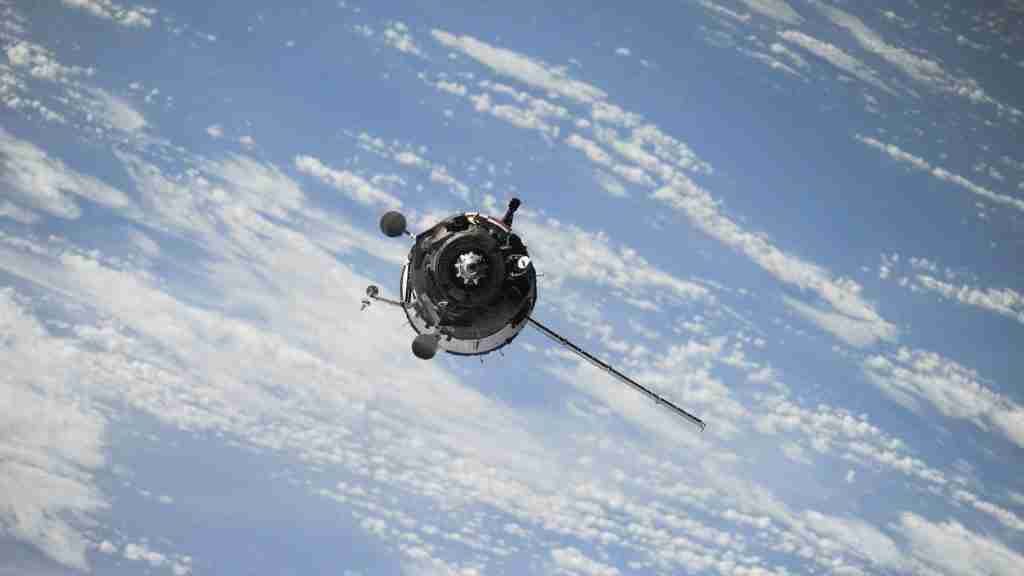

In 2014, after 10 long years of space travel, the Rosetta spacecraft achieved a major SCI-FI-worthy milestone.
It became the very first artificial human construct to make a successful landing on Comet 67P. This exciting feat had never before been accomplished anywhere in our Solar System.
The journey from its origin to its destiny was fraught with unchartered territory and scientists around the globe held their breath while this remarkable craft set out on a historical mission of exploration.
9. The First spacecraft to visit Pluto was New Horizons, which flew by in 2015.
New Horizons was the first spacecraft ever to visit the distant dwarf planet, Pluto. In 2015, it flew by this outermost planet in our solar system.
This huge milestone marked an incredible step toward space exploration and undeniably shaped the technological future of astronomy.
New Horizons was launched in 2006, taking almost ten years for it to complete its journey to discover this seldom-explored region of space. This overnight success has shed new light on Pluto and its place among the other planets in our solar system.
10. The First spacecraft to land on Mars was the Viking 1 lander in 1976.
In 1976, history was made with the descent of the Viking 1 lander on Mars. It marked a watershed moment for space exploration, becoming the first spacecraft to touch down on the red planet.
This tactical task surpassed lofty expectations put forth by experts in the field, ushering in a new era of interplanetary technology and exciting possibilities.
For more than four decades since then, scientists have continued to build upon this ambitious space mission, leading to new discoveries and constructing a lengthy aviation archive that will soon experience great expansion within our solar system.
11. First human landing on the Moon was the Apollo 11 mission in 1969.
The Apollo 11 mission marked a major milestone in human history; the first human landing on the Moon.
On July 16th, 1969, millions of people across the world watched Neil Armstrong make history as he took that record-breaking first step off the ladder and onto our planet’s only celestial buddy in awe.
A small but successful beacon of light, filled with fun facts about space exploration, serves as a reminder of humanity’s remarkable ability not to limit its bounds within itself, but rather to look elsewhere for feats hardly achievable.
12. The First woman to walk on the Moon was astronaut Peggy Whitson.
On the Apollo 17 mission in 1972, astronaut Peggy Whitson created history as she became the first woman to walk on the Moon.
This thrilling accomplishment stands out amongst her plethora of other achievements including a doctorate degree in biochemistry and several awards from NASA.
8 days before Peggy’s historical journey, another woman named Rhea Seddon was sent into space alongside three fellow Astronauts. Although this mission predates her own, unfortunately, it did not equate to a Moon landing.
This paved the way for astronomical boundaries to be broken as a significant milestone had been accomplished. Peggy Whitson has made a remarkable mark in space exploration that continues to open up diverse possibilities for today’s and tomorrow’s female astronauts alike.
13. The First spacecraft to land on Venus was the Venera 7 lander in 1970.
In 1970, a great milestone in the exploration of space was achieved: the first successful landing on Venus. The Soviet to be credited with this remarkable feat is the Venera 7 lander.
This vehicle braved the unparalleled elements surrounding Venus: an air pressure around 90 times that of Earth’s, acidic clouds and an intense temperature of 462 degrees Celsius were no match for its design. After it descended through the outer atmosphere, the spacecraft was safely planted onto the planet’s surface with a successful soft landing.
Its courage and technical capabilities make it truly admirable. Since its triumph over Venus, many other foreign bodies have been explored by Venera 7’s successors, further twirling man’s tight grip upon nature itself.
It set in motion a legacy of remarkable achievements within our solar system as each orbiter slowly unravels another layer of secrecy… leaving no stone unturned!
14. The First spacecraft to visit Mercury was Mariner 10, which flew by in 1974.
In 1974, history was made when Mariner 10 became the first spacecraft to visit Mercury. The flyby lasted for 35 minutes and Mariner 10 went on to fly by the planet twice more in March of 1974.
Data collected during these brief encounters unlocked a vast new area of space exploration, revealing fascinating fun facts about space exploration, from the planets never before seen up close. Onboard equipment was able to capture pictures, analyze data, and scientific measurements to learn a great deal about our closest cosmic neighbor.
Thousands of images were sent back that gave us an insight into Mercury’s water vapor atmosphere and enormous craters formed over billions of years. This served as a breakthrough in knowledge concerning these close to us unexplored worlds above our skies.
15. The First spacecraft to orbit Mercury was MESSENGER.
In 2011, MESSENGER began its expedition to be the first spacecraft to reach Mercury—a remarkable feat.
The probe’s objective was to gather valuable data from the planet closest to the Sun.
Guided by its sturdy structure and powered by innovative groundbreaking technology, MESSENGER’s voyage around Mercury continued for four glorious years until 2015 when it finally entered the pages of history books.
16. The First spacecraft to visit Saturn was Pioneer 11, which flew by in 1979.
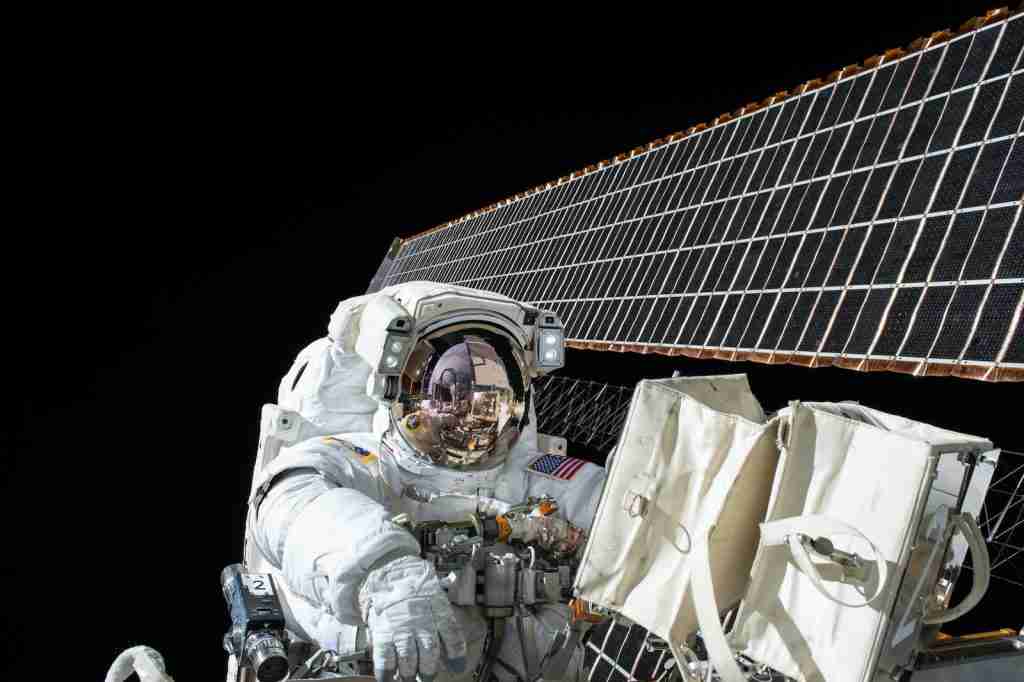

with Saturn in 1979!
In 1979, Pioneer 11 became the first spacecraft to visit Saturn. It was quite an accomplishment for those involved in the project, as this piece of equipment had to endure several astronomical miles just to enter the orbit of the ringed planet.
It was considered mission success just to make it that far! But Pioneer 11’s expedition did not end there.
This spacecraft was able to observe many aspects of Saturn and even though it could only get so close, its destination flyby provided remarkable insight into the futuristic twelfth Zodiac sign from Earth.
17. The First spacecraft to orbit Saturn was the Cassini spacecraft, which orbited the planet from 2004-2017.
In 2004, a feat of incredibly advanced space exploration was achieved when the Cassini spacecraft became the first-ever spacecraft to orbit Saturn.
Experiencing gravity pulls and planetary devices so closely related to that of Earth, images from there gained a massive amount of information paving the way for further research as it circled around the planet’s sky in an array of adventures aiding technology and thoughtful methodology from scientists over 13 years.
18. The First spacecraft to visit Uranus was Voyager 2, which flew by in 1986.
In 1986 the first spacecraft to ever visit Uranus put through motion its exciting mission. Voyager 2 sailed silently throughout space, already responsible for explorations of Jupiter and Saturn in its previous beneficial geographic observations.
After entering deep within our solar system, bravely bartering unknown territory beyond all expectation, it found itself close within range of the quirky mysterious giant gas giant planet.
Using its conveniently prepared knowledge since studying nearby planets for over a decade before arriving in Uranus’ orbit, scientists had great hope that a comprehensive collection of invaluable data about this untouched area would be acquired by spacecraft.
19. The First spacecraft to visit Neptune was Voyager 2, which flew by in 1989.
Over 30 years ago, in 1989, Voyager 2 made history as the first-ever spacecraft to visit Neptune. At the time, few knew what was ahead for the mission team.
They set sail on a path to explore this mysterious planet for the very first time. Since then, humans have been able to create a clear picture of the enchanting place existing billions of miles away from our own homes.
Scientists, along with audiences around the world, were mesmerized as they delved into fascinating fun facts about space exploration. It continued through uncharted waters into a new era of exploration and discovery. Its feat demonstrated our expanding understanding and reach of what lies beyond Earth’s boundaries.
20. The First spacecraft to visit the dwarf planet, Ceres, was Dawn.
In March 2015, an amazing milestone was achieved when Dawn, the first spacecraft was sent to the dwarf planet Ceres.
This craft entered an orbit around this distant world and over the next three years brought scientists closer than ever before to its mysterious terrain. During this time period, Dawn acquired an abundance of scientific data from instruments and other means.
Astonishing images and information about the dwarf planet’s geology were revealed as it ranged in distance from thousands of kilometers to extremes prompting revolutionary research conducted into its history and structure.
21. The First spacecraft to visit the dwarf planet, Pluto, was New Horizons, which flew by in 2015.
The momentous Milestone in space exploration was finally reached in 2015 when New Horizons became the first spacecraft to visit the dwarf planet, Pluto.
It marked a seismic shift in human understanding of the outer solar system and opened up the possibilities for further interplanetary exploration. The mission was highly ambitious, as up until this point, no other space vehicle had even attempted a fly-by with such a small known object.
Thankfully, all preparations went according to plan and an ecstatic team of scientists cheered as New Horizons crossed Pluto’s orbit and pinged back the first signs of its successful trajectory.
It truly echoed an epic conclusion to this decades-long quest that once seemed an epochal impossibility.
22. The First spacecraft to visit the Kuiper Belt, a region of our solar system beyond Neptune, was New Horizons, which flew by the dwarf planet, Pluto, in 2015.
NASA’s New Horizons mission was the first spacecraft ever to travel to the Kuiper Belt—a wide expanse of mysterious space located beyond Neptune.
This historic mission made waves when it flew by dwarf planet Pluto in 2015, an event that stands as one of the most momentous landmarks for space exploration.
New Horizons marked a distinct turning point that opened up deep space to researchers worldwide, making history when it revealed what nobody had seen before—the secrets of the Kuiper Belt.
23. The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest spacecraft ever built.
One of the fun facts about space exploration is that many intrepid astronauts of numerous nations call the largest spacecraft in history their home: the International Space Station (ISS). This notable feat of modern technology has been aptly deemed ‘the millennial ark’, a testament to its indescribable grandeur.
The innovative vessel completely revolutionized space technology, reaching distances unimaginable 2025 years ago. Signatories from five g acquiring nations developed a supportive base for those striving for galactic exploration, ultimately enabling dockings with unprecedented scientific curiosity and exploration far off in outer space.
Indeed, countless astronauts annually embark on unprecedented rocket rides to explore unchartered territories beyond Earth’s limited boundary.
24. The International Space Station (ISS) orbits Earth at an altitude of about 250 miles (400 kilometers).
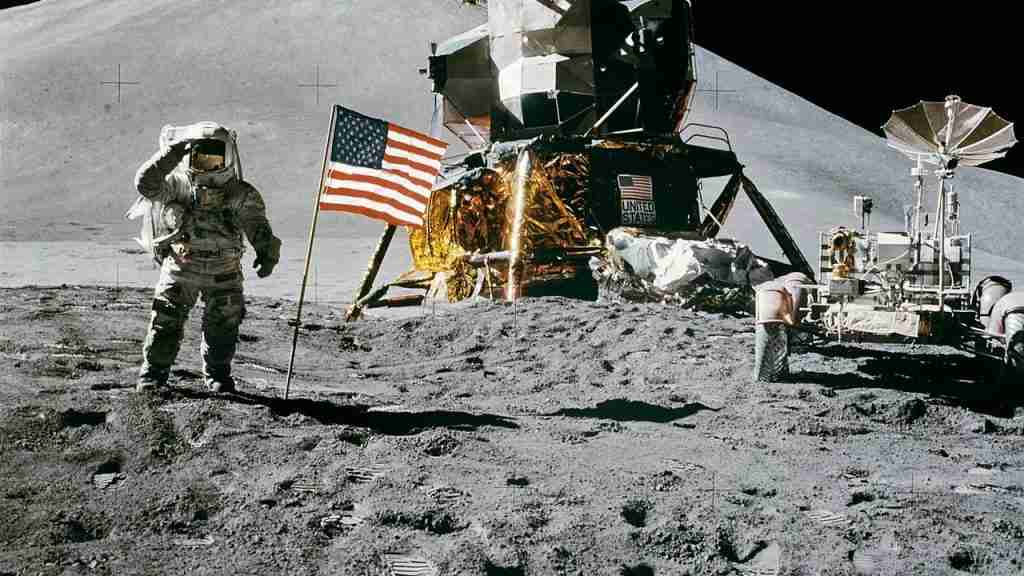

At a majestic altitude of 250 miles (400 kilometers), the International Space Station (ISS) can be seen soaring high above Earth’s atmosphere.
This engineering masterpiece has become something of an iconic orbital landmark, the gateway to humankind’s space exploration since its launch two decades ago.
From our terrestrial reality below, many avid observers rapidly point their instruments towards these hallowed heights to admire them as it whizzes around the earth.
Constantly consolidating our knowledge base and understanding of this unknown space environment always furthers our knowledge of the cosmos beyond.
25. The International Space Station (ISS) weighs about 925,000 pounds (420,000 kilograms).
The International Space Station clocks in with an impressive weight of 925,000 pounds. That’s an astounding 420,000 kilograms, putting it in the same heavyweight category as 320 standard-size cars!
Clearly, this vast human-manufactured hub boasts mass for miles and is making its mark orbiting throughout our planet’s lower atmosphere.
One can only imagine all the objects contained within that equate to up to these large, jaw-dropping numbers.
26. The First spacecraft to visit the sun was the Parker Solar Probe, which launched in 2018.
The remarkable journey of the Parker Solar Probe began in 2018. This revolutionary spacecraft was created with the most sophisticated instruments and technologies ever designed, enabling it to withstand the scorching environment of the sun.
Powered by a Delta IV Heavy rocket, it soared into its component parts during launch. In an endeavor to unravel a realm of mysteries about our closest star, the Parker Solar Probe visited darker areas of space en route to explore what is basically an unexplored wilderness.
The unmistakable heat messages it receives every second make moments like these unique. Just think: humans have built a tiny ship that will ride on its own radiation right up to points near to touching this celestial body and stay untamed, smashing laws of nature while exploring some extreme conditions to complete an astonishing mission.
27. The Parker Solar Probe is the fastest spacecraft ever built.
Scientists at NASA have outdone themselves with the epic success of their crowning achievement — the Parker Solar Probe! It is officially the fastest spacecraft ever created and delivered, bringing mankind closer to harnessing the energy of our own Sun.
With an incredible speed of up to 430 000 miles per hour (690 000 kilometers per hour), it can travel faster than a speeding bullet. Just imagine its intrepid journey toward unraveling the secrets of our star!
The Parker Solar Probe opens vast possibilities for discoveries still lurking within the magnetic fields of our nearby heliosphere which is one of the fun facts about space exploration.
28. There have been six manned missions to the Moon.
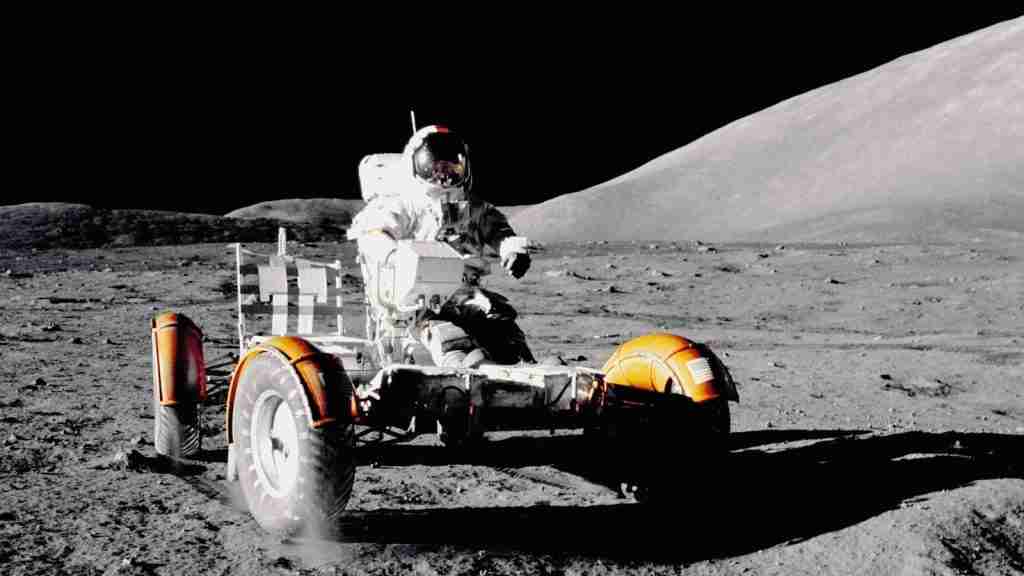

NASA has boasted six successful manned missions to the Moon since the 50s. All of these missions were part of the Apollo program, an enormous effort that was dedicated to the exploration and study of the lunar surface.
The missions began in 1969, with NASA sending three astronauts aboard the spacecraft Apollo 11, who were the first human beings ever to land on –and set foot– on the surface of our closest celestial neighbor.
A second mission came six months later when Apollo 12 landed near its predecessor’s landing site. This marked only two out of six more exciting voyagers made over a four-year span until 1972 when the powerful Saturn V rocket connected mankind with space and left us filled with awe and inspiration.
The last manned mission to the Moon was the Apollo 17 mission in 1972.







