25 Fun Facts About The Ocean | Seaside Secrets
1. The ocean covers more than 70% of Earth’s surface.
Earth is often called the ‘Blue Planet’ due to this extensive coverage.
The vastness of the oceans makes them the most prominent feature of our planet. This coverage has a profound impact on Earth’s climate and ecosystems.
2. The Pacific Ocean is the largest ocean on Earth.
It stretches from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south.
Covering more than 60 million square miles, the Pacific Ocean is larger than all of Earth’s land area combined. Its size and depth create diverse marine habitats.
3. Oceans hold 97% of Earth’s water.
Most of Earth’s water is salt water in the oceans.
This vast quantity plays a crucial role in supporting life and influencing climate. The immense volume of water is a key component of Earth’s hydrosphere.
4. Mariana Trench is the deepest part of the ocean.
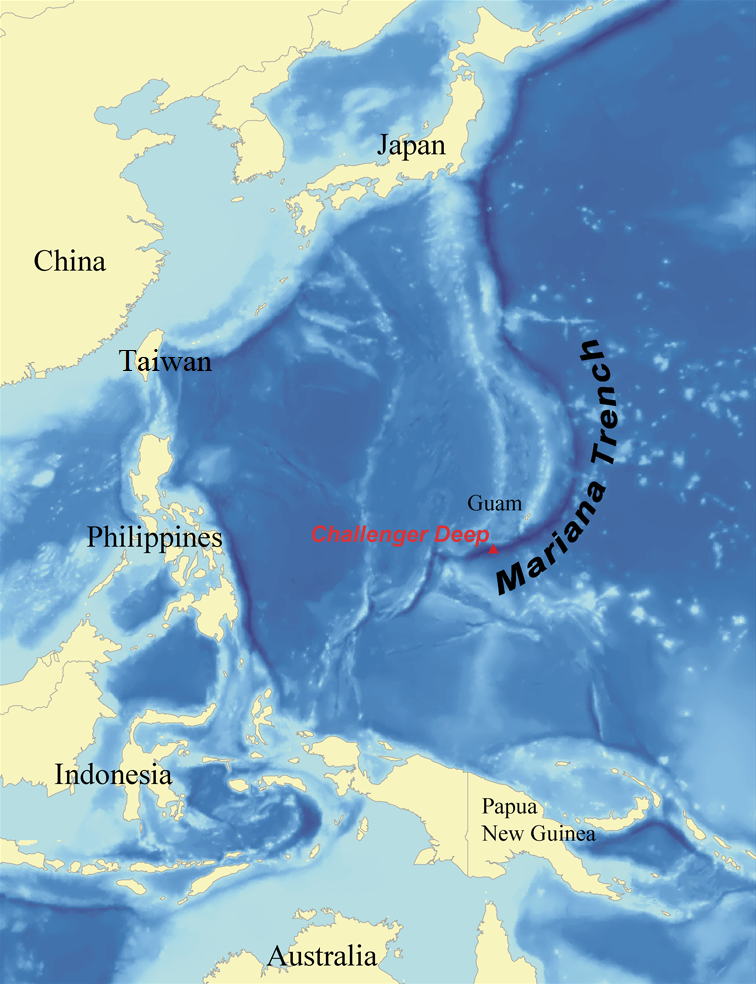
Located in the western Pacific Ocean, the trench reaches depths of about 36,000 feet.
This depth is more than the height of Mount Everest. The trench remains one of the least explored areas on Earth.
5. The Great Barrier Reef Is the largest living structure on Earth.
It’s located in the Coral Sea, off the coast of Australia.
The reef is so large it can be seen from space. It’s home to diverse marine life and is a critical marine habitat.
6. The ocean is home to the world’s longest mountain range.
The Mid-Ocean Ridge stretches about 40,000 miles across the ocean floor.
This underwater mountain range is largely unexplored. It plays a key role in seafloor spreading and plate tectonics.
7. There are more historical artifacts under the sea than in all of the world’s museums.
Countless shipwrecks and ruins lie on the ocean floor.
These artifacts offer a glimpse into human history and ancient trade routes. The deep sea preserves these remnants in remarkable condition.
8. Over 80% of the ocean Is unexplored and unmapped which is one of interesting Fun Facts About the Ocean.
Despite advances in technology, vast areas remain mysterious.
Exploring these regions could reveal new species, geological formations, and insights into our planet’s history. The ocean’s depths hold many undiscovered secrets.
9. The ocean is a major source of food for humans.
It provides a significant portion of the world’s protein intake.
Fisheries and aquaculture are crucial for global food security. Sustainable practices are essential to maintain these resources.
10. The majority of Earth’s oxygen comes from the ocean.
Microscopic plants in the ocean provide most of the oxygen we breathe.
Phytoplankton, tiny marine plants, produce oxygen through photosynthesis. They are as important as land-based plants for our atmosphere.
11. The ocean regulates Earth’s climate.
It absorbs solar radiation and distributes heat around the planet.
Currents and large water bodies play a vital role in maintaining Earth’s temperature balance. This regulation is crucial for sustaining life as we know it.
12. How many oceans are there?
Officially, there are five oceans on Earth. These are the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic Oceans.
13. The ocean floor is as varied and diverse as the land terrain.
It features mountains, valleys, plains, and volcanoes.
This underwater landscape is shaped by geological processes similar to those on land. It’s a dynamic environment with ongoing changes and formations.
14. Bioluminescence is a common feature in deep-sea creatures.
Many ocean animals produce light through chemical reactions.
This adaptation is used for attracting prey, communication, and defense. The deep sea’s darkness is often lit by these glowing organisms.
15. Hydrothermal vents support unique ecosystems.
These vents release heated water and minerals from Earth’s crust.
Located in the deep sea, they create habitats for specialized life forms. These organisms thrive without sunlight, relying on chemosynthesis.
16. The ocean has its lakes and rivers.

These underwater bodies of water have higher salt content and density.
Found deep within the ocean, these lakes and rivers are fascinating ecosystems. They host unique life forms adapted to extreme conditions.
17. The speed of sound is faster underwater than in the air.
Sound waves travel more efficiently through denser mediums.
Marine animals utilize this property for communication and navigation. It’s also important for submarine and underwater research technologies.
18. Underwater volcanoes release molten rock and gases.
These eruptions contribute to the formation of new seafloor.
Submarine volcanoes are a significant part of Earth’s geologic activity. They contribute to the formation of islands and new marine habitats.
19. Coral reefs are among the most diverse ecosystems on Earth.
They are often referred to as the ‘rainforests of the sea.’
Coral reefs support a vast array of marine life, offering food, shelter, and breeding grounds. Their biodiversity is vital for ecological balance and marine health.
20. The ocean absorbs carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.

It acts as a natural carbon sink, helping to mitigate climate change.
However, increased CO2 absorption leads to ocean acidification, affecting marine life. This balance is crucial for the health of ocean ecosystems.
21. The ocean has a profound impact on weather patterns.
It influences weather systems like hurricanes and monsoons.
Ocean currents and temperatures play a key role in weather formation and intensity. Understanding these patterns is essential for predicting weather events.
22. The ocean is a treasure trove of natural resources.
It provides minerals, oil, gas, and renewable energy sources.
Marine resources are vital for economic development and technological advancements. Responsible exploration and usage are key to sustainability.
23. The ocean’s salinity varies in different regions.
Factors like evaporation, freshwater input, and ice melting affect salinity levels.
Salinity influences ocean currents, marine habitats, and the distribution of life. This variation is an important aspect of marine science studies.
24. The ocean is home to the largest animal on Earth.
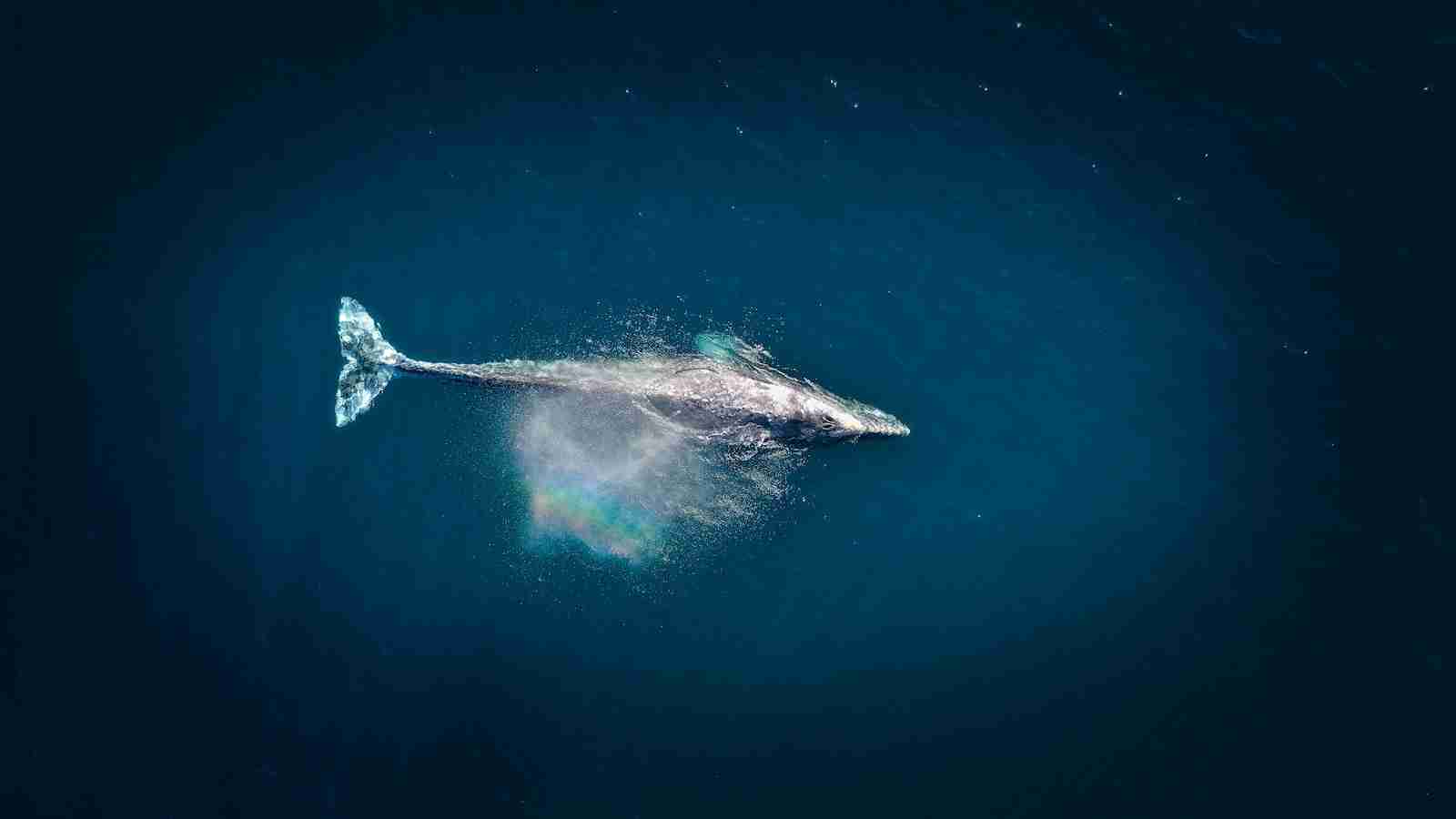

The blue whale is the largest animal ever known to have existed.
These magnificent creatures can grow up to 100 feet long. Their size is a testament to the vastness and richness of marine ecosystems.
25. The ocean has a rich cultural and historical significance.
It has been a source of inspiration, exploration, and sustenance for civilizations.
The ocean’s influence can be seen in art, literature, and history. Its role in human development is as profound as its ecological importance.
FAQs
The depth of the sea varies greatly, with the average ocean depth being about 12,080 feet (3,682 meters). The deepest part of the ocean is the Mariana Trench, which reaches depths of over 36,000 feet (nearly 11,000 meters).
There are five major oceans on Earth: the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern (Antarctic), and Arctic Oceans.
Oceans can be extremely deep. On average, the ocean’s depth is about 2.3 miles (3.7 kilometers), but this can vary greatly across different regions.
While the ocean can be intimidating due to its vastness and the unknown creatures it harbors, it is also a place of great beauty and scientific interest. Respect and understanding can help mitigate fears
An ocean is a large body of salt water that covers about 71% of Earth’s surface. It plays a crucial role in climate regulation, supports a diverse range of life forms, and is key to global economies.







